A Comprehensive Guide to Choose Safety Light Curtains
- Share
- Issue Time
- Apr 17,2024
Summary
This article discusses the key factors to consider when selecting a light curtain, and provides a step-by-step guide to help choose the right light curtain.
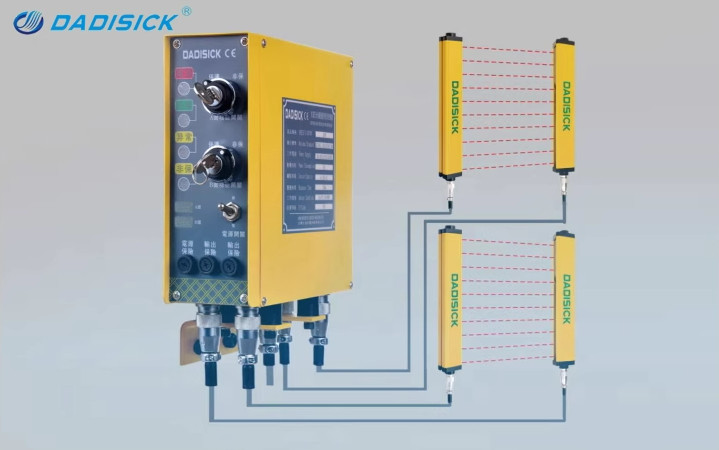
The Main Components of Light Curtain
1. Transmitter — The light curtain system consists of a transmitter that emits multiple beams of infrared light or visible light, creating an invisible safety barrier.
2. Receiver — Corresponding to the transmitter, the receiver is equipped with photoelectric sensors capable of detecting each beam of light by the transmitter.
3. Mounting Brackets — The mounting bracket allows for proper alignment of the transmitter and receiver, which is key to ensuring the system accurately detects intruding objects.
4. Connection Cables — Connection cables play a crucial role in the functionality and reliability of safety light curtains. They are responsible for ensuring that power and communication signals are effectively transmitted between various components of the system. Here are some critical aspects of their role:
● Power Supply — They deliver the necessary power from the source to the light curtain's transmitter and receiver units, ensuring that the system remains operational.
● Data Transmission — Connection cables facilitate the transfer of data between the light curtain units and the control system.When the light beams are interrupted, indicating an object's presence, this information is sent via the cables to the control unit, which then processes the signal and triggers a predefined safety response.
● System Integration — These cables enable the integration of the safety light curtain with other machine safety components or control systems, allowing for coordinated actions and comprehensive protection strategies.
● Diagnostics and Communication — Connection cables can transmit diagnostic information from the light curtains to monitoring systems, helping identify issues such as alignment problems, beam blockages, or system faults, ensuring timely maintenance and minimizing downtime.
All these components work together to form an invisible beam-Protecting Barrier
When an object, such as a person's hand or body, interrupts one or more of the light beams, the receiver unit detects this interruption (Each beam has a corresponding sensor in the receiver unit), this information is sent via the cables to the control unit, which then processes the signal and triggers a predefined safety response.
The safety light curtain (AOPD: Active Optoelectronic Protective Devices) is more efficient compared to traditional industrial protective devices.
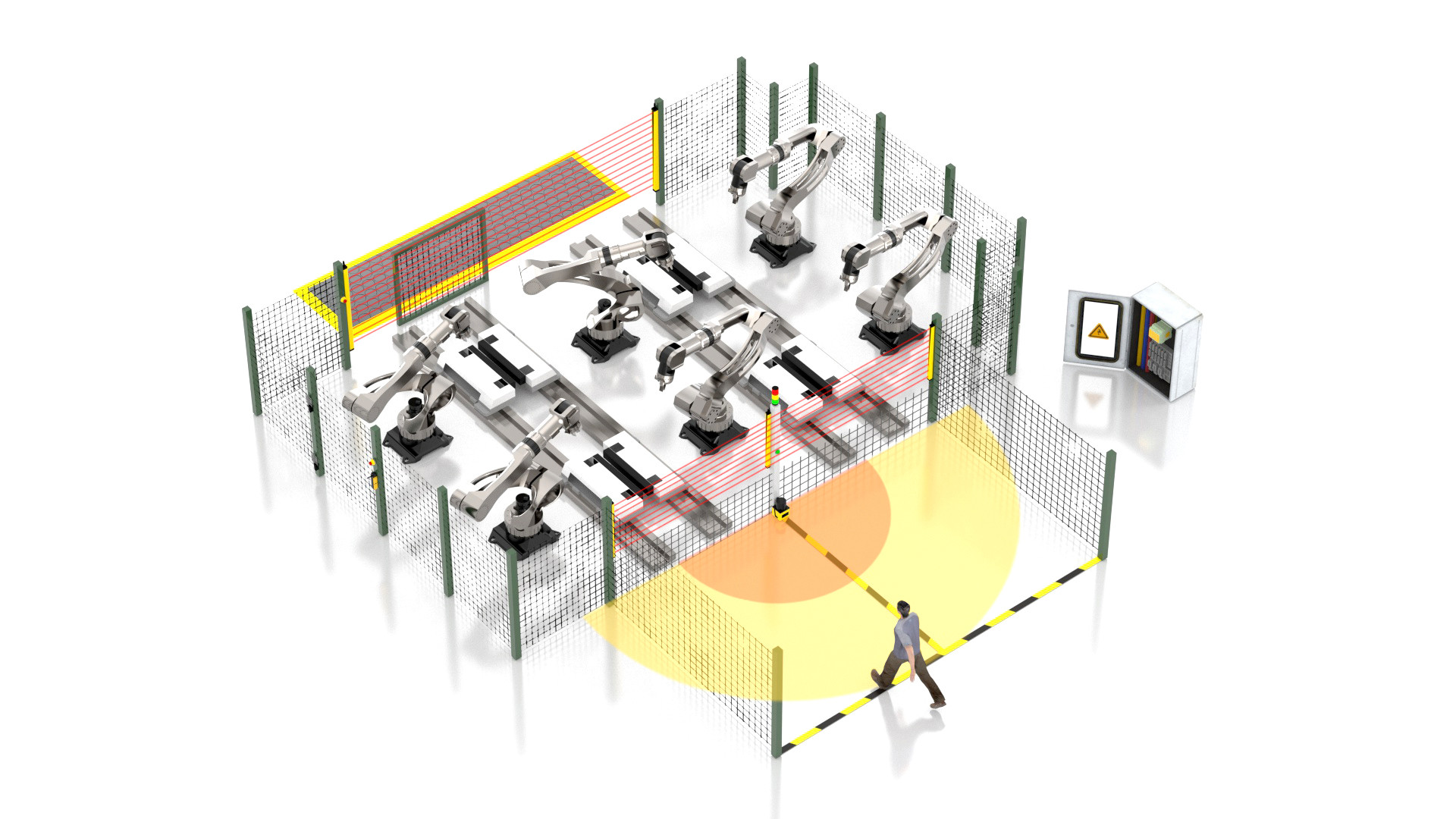
Applications of Light Curtain
The world's first safety light curtain product was born in 1952 and has a history of more than 70 years. Safety light curtains and related products have formed a stable industrial system, the technology has become increasingly mature, and they are widely used in many fields.
Since 2006, DADISICK has been committed to the production and research and development of safety light curtains for 18 years. With excellent manufacturing strength and competitive prices, DADISICK provides a series of high-quality safety light curtain products to customers around the world. During the production process, DADISICK always puts quality assurance first and adheres to international standards to ensure that its products can meet the strict requirements of the global market. Listed below are several major application scenarios of safety light curtains that we have summarized from our growing customer experience.
● Manufacturing Plants — They are installed around machinery that poses a potential threat, such as hydraulic presses or robotic welding arms, to prevent operator injury.
● Assembly Lines — Safety light curtains can detect unauthorized access or a limb reaching into a hazardous area, halting the assembly line to prevent accidents.
● Packaging Industry — They ensure that if someone reaches into a machine for any reason, like during maintenance or to clear a jam, the machine stops to prevent injury.
● Automotive Industry — Utilized around heavy and robotic assembly units to protect workers from the moving parts.
● Material Handling — Installed around conveyor systems to stop the conveyor if a person or object is detected in a dangerous area.
● Machine Tooling — They safeguard operators from injuries caused by the operation of cutting, molding, or pressing machines.
● Pharmaceuticals and Food Processing — Used to maintain hygiene by minimizing human contact with products and to ensure safety around machinery.
● Woodworking and Metalworking — To protect against machinery such as saws, presses, and shearing machines that can cause severe injuries.
● Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems — They help in access to moving parts within these systems.
● Clean Rooms — In settings that require contamination control, they restrict entry and maintain environmental integrity.
● 3D Printing — Ensuring the safety of operators from moving parts within large-scale industrial 3D printers.
● Elevator and Escalator Industry — To detect objects or persons in the path of moving doors or steps, preventing entrapment or injury.
Several Important Aspects to Consider When Selecting A Light Curtain
Step 1: Select the safety level of the safety light curtain according to the degree of danger your equipment poses to people (In short: Type 4 is designed for higher-risk conditions, Type 2 is suitable for lower-risk environments). The picture on the right shows the selection criteria for security levels.
The safety light curtains produced by DADISICK have obtained multiple international certifications.
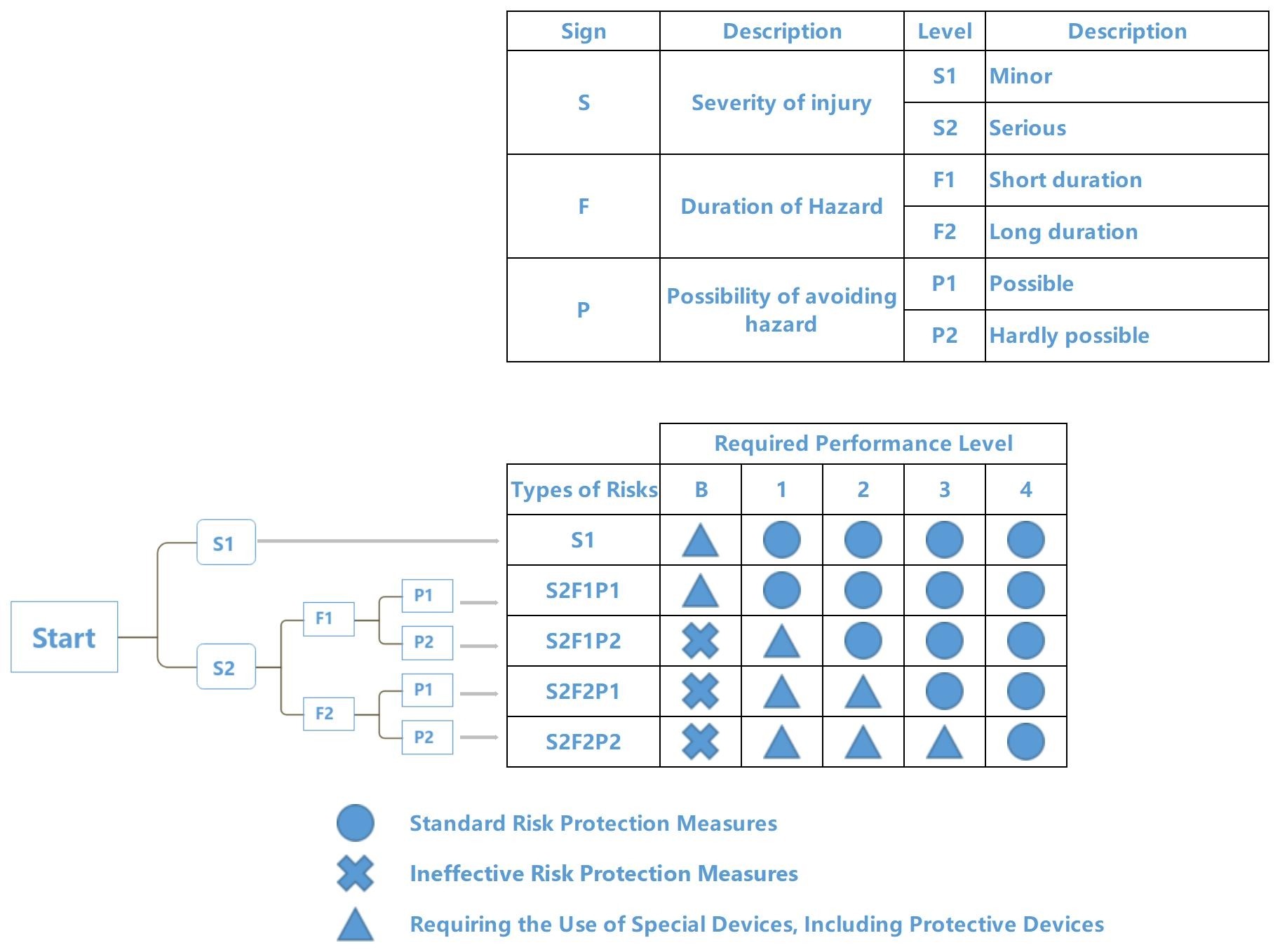
Step 2: Determine the size of the safety distance (the vertical distance from the protective barrier formed by the safety light curtain to the hazard source).
Step 3: Select the optical axis spacing. For finger protection, a spacing of 10mm is typically chosen; for palm protection, 20mm is common; for foot or body protection, a spacing of 40mm is generally selected. However, these principles may not apply when the safety distance is large. The principle is to ensure that the equipment can stop before a person reaches the hazard source.
Step 4: Select an appropriate number of optical axes based on your protection height (an even number greater than 4).
Step 5: Consider the response time of the light curtain, determining how quickly the curtain needs to detect and respond to potential hazards. A fast response time (usually measured in milliseconds) is crucial for minimizing the risk of accidents.
Step 6: Select the type of signal output (such as PNP*2, NPN*2, Safety Relay).
Step 7: Select the beam spacing (for safety light curtains with smaller cross-sectional dimensions, the beam spacing is typically closer, less than 3 meters; for those with larger cross-sectional dimensions, the beam spacing is generally farther, greater than 3 meters)
Step 8: Select the synchronization mode between the emitter and receiver (optical synchronization: no connection between the emitter and receiver; wire synchronization: a wire connection between the emitter and receiver).
Step 9: Choose the structural type of the safety light curtain. Decide whether to opt for a larger or thinner profile, and whether a blind-zone-free safety light curtain is needed.
Step 10: Choose the installation method (multiple installation options available, including L-shaped side mounting, L-shaped top and bottom mounting, steel pipe bracket mounting, and end cap with built-in mounting holes, etc).
Step 11: Consider whether the safety light curtain needs to be resistant to electromagnetic interference, arc and laser interference, as well as daylight interference, and whether it needs to be waterproof and dustproof, based on your equipment's operating environment.
Installation of The Light Curtain
● Strictly adhere to the installation manual.
● Choose a light curtain suitable for your equipment type and protection requirements.
● Select appropriate drilling positions to avoid diminishing the protective effect due to incorrect hole placement.
● Maintain a certain distance between two sets of light curtains during installation to prevent mutual interference if they are too close.
● After installation, test whether the light curtain can start properly and assess its protective effectiveness.
Customer Service
When you find yourself indecisive about which brand of safety light curtain product to choose, consider opting for DADISICK. We have compiled a product guide comparing the performance of safety light curtains from different brands. Factors such as response time, detection accuracy, durability, and more are included for consideration.
DADISICK offers brand replacement services and provides performance comparison documents for safety light curtains from various brands. This can help you easily find the most suitable option among the many brands available.
Future Development Trends in The Field of Light Curtains
Safety light curtain technology, as a crucial technology ensuring safe human-machine interaction, will see future development trends closely related to intelligence, adaptability, communication interoperability, flexibility and customizability, as well as energy efficiency and environmental protection.
With the continuous advancement of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, safety light curtain technology will become more intelligent and adaptive. This means that light curtain systems will not only be able to detect and prevent potential hazards in real-time but also adjust and optimize themselves according to changes in the working environment to better adapt to complex industrial environments.
In the future, safety light curtain technology will place more emphasis on communication and interoperability with other devices. Through close integration with other systems such as robots and automation equipment, light curtain systems can achieve more efficient information sharing and collaboration, thereby improving the efficiency and safety of the entire production line.
In terms of flexibility and customizability, future safety light curtain technology will focus more on meeting the needs of different industrial applications. The shape, size, and installation method of light curtains will be more adjustable to meet the requirements of various work environments. This will make safety light curtains more flexible and practical, suitable for a wide range of industrial scenarios.
Additionally, energy efficiency and environmental protection are also important directions for the future development of safety light curtain technology. By adopting more energy-efficient technologies and materials, as well as implementing intelligent power management, the energy efficiency of light curtain systems will be significantly improved, and operating costs will be effectively reduced. Moreover, this will help reduce environmental impact and promote the sustainable development of industrial production.
Finally, with increasing global attention to industrial safety, the future development of safety light curtain technology will be driven by global standards and regulations. Establishing unified safety standards will help improve the consistency and comparability of safety light curtain systems within the industry, promoting the standardized development of technology.