AGV Mobile Robot with Ultrasonic Radar Collision Avoidance Sensor
- Share
- publisher
- Zoe
- Issue Time
- Sep 25,2024
Summary
The integration of ultrasonic radar collision avoidance sensors in Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is an essential safety feature. These sensors utilize ultrasonic technology to monitor the surrounding environment in real-time, effectively avoiding collisions with obstacles. Below, we will detail the working principle, advantages, and practical applications of ultrasonic radar collision avoidance sensors in AGVs.
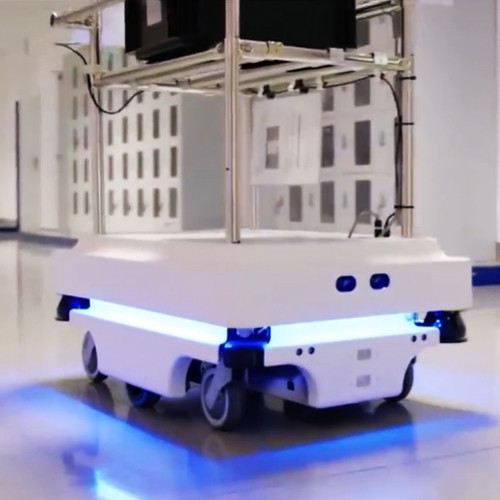
Ultrasonic Radar Collision Avoidance Sensors in AGVs
The integration of ultrasonic radar collision avoidance sensors in Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is an essential safety feature. These sensors utilize ultrasonic technology to monitor the surrounding environment in real-time, effectively avoiding collisions with obstacles. Below, we will detail the working principle, advantages, and practical applications of ultrasonic radar collision avoidance sensors in AGVs.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors work by emitting high-frequency sound waves (typically above the human hearing range) and receiving the signals reflected back from surrounding objects. The sensor consists of a transmitter and a receiver; the transmitter emits ultrasonic waves, which reflect off objects and are received by the receiver. By measuring the time difference between emission and reception, and using the speed of sound (approximately 340 meters per second in air), the distance to the object can be calculated. (Learn more about ultrasonic sensors )
Advantages of Integrating Ultrasonic Sensors into Collision Avoidance Systems
• Surface Insensitivity: Unlike optical sensors, ultrasonic sensors do not depend on the surface color, gloss, or texture of objects, allowing for stable detection of various materials.
• Strong Adaptability: Ultrasonic sensors continue to function well in environments with dust, fog, and low light, where optical sensors may be severely affected.
• Cost-Effectiveness: Ultrasonic sensors are generally less expensive than laser or radar sensors, making them suitable for large-scale deployment in AGVs and other automation equipment.
Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors in AGV Robots
• Forward Path Detection: Ultrasonic sensors installed at the front of the AGV detect obstacles in the path ahead, such as pedestrians, other vehicles, or stationary objects. If an obstacle is detected within a preset safety threshold, the AGV will issue an alarm or automatically slow down/stop to avoid a collision.
• Reverse Path Detection: Ultrasonic sensors mounted at the rear of the AGV detect obstacles when reversing, ensuring safety during backward operations.
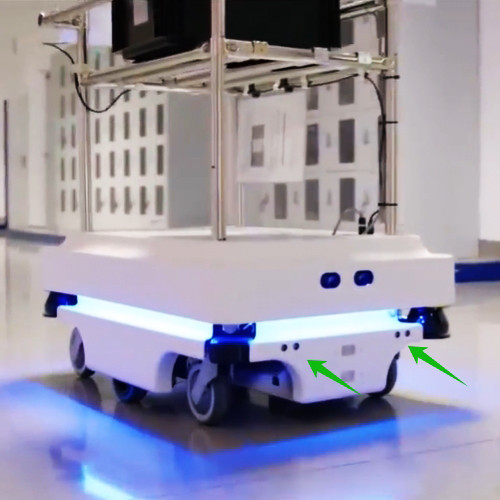
Integration of Ultrasonic Sensors with Mobile Machinery Systems
Ultrasonic sensors are typically integrated into the AGV's control system, communicating with the main control unit via serial or digital I/O interfaces. The control system makes obstacle avoidance decisions based on the distance information returned by the sensors, combined with the AGV's current position, speed, and pre-set safety rules and path planning.
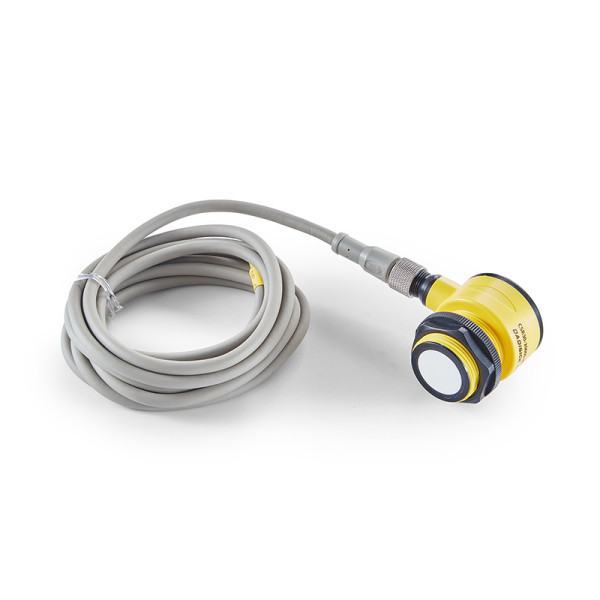
Recommended Ultrasonic Sensor
Main Features
• Full metal M30 mounting threaded sleeve
• Suitable for harsh environments
Basic Features
• 1 NPN or PNP switch output
• 2 NPN or PNP switch outputs
• Analog voltage output of 0-10V or analog current output of 4-20mA
• Supports the latest 10-Link output and digital RS485, Modbus-RTU standard protocol communication
• Detection distance learning function via gray wire
• Standard operating voltage of DC 10-30V
• Temperature compensation
Considerations for Ultrasonic Sensors
• Blind Spot Issues: Ultrasonic sensors may have detection blind spots at very close distances; this factor should be considered during design to avoid collisions in these areas.
• Multi-Sensor Collaboration: To improve detection accuracy and reliability, multiple ultrasonic sensors can be installed on the AGV, and other types of sensors (such as infrared, laser, or radar) can be integrated for comprehensive judgment.
• Environmental Adaptability: The speed of ultrasonic waves may vary in different environments (e.g., temperature and humidity changes), necessitating calibration or algorithm adjustments for compensation.
Related Non-Contact Sensors
Output method: NPN/PNP+analog+RS485
Resolution: 1mm
Laser type: red semiconductor laser Class II laser 655+10nm<1m
Reaction time: 50-200ms
Sensing range 20m, A technique that uses a laser beam to measure distance and create detailed maps of objects and environments.
Beam spacing: 40mm<br>
Number of optical axes: 72<br>
Protection height: 2840mm<br>
Laser curtain sensor outputs (OSSD)2 PNP
Detection range: 100-2000 mm, 150-3000 mm
Material: plastic accessories, filled with epoxy resin
Connection type: 5-pin M12 connector




