How Do Different Modes of Photoelectric Switch Sensors Work? A Comprehensive Explanation!
- Share
- publisher
- Zoe
- Issue Time
- Feb 17,2025
Summary
Photoelectric sensors mainly have three common working types: Diffuse Reflective, Specular Reflective, and Through-Beam. Each type has different working principles and application scenarios, catering to various industrial needs.
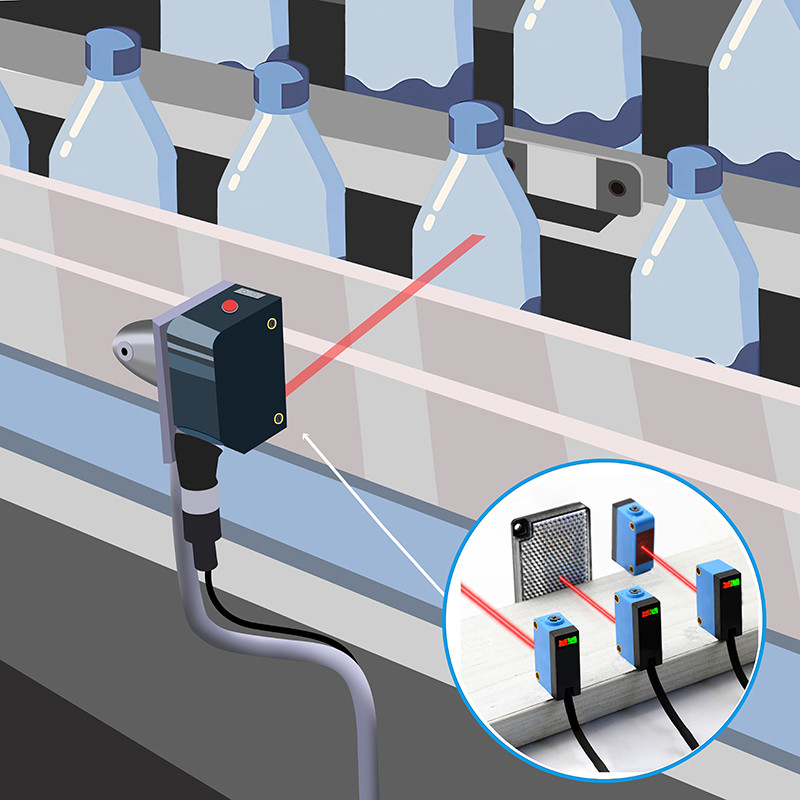
What is a Photoelectric Sensor?
A photoelectric sensor is a type of switch that detects changes in light (such as intensity, reflection, or obstruction) and converts these changes into electrical signals. Its operation is based on detecting the presence or variation of light to control the system.
The main feature of photoelectric sensors is their "non-contact" operation. They do not require direct contact with the object being detected; instead, they use light emission and reception to detect the presence, position, or changes of objects. This characteristic makes photoelectric sensors widely used in various industrial applications, especially in automated production lines, object detection, and safety protection systems.
The core formula for a photoelectric sensor is:
Detection ability = f (light intensity, object reflectivity, environmental interference, detection distance).
How Do Different Modes of Photoelectric Switch Sensors Work?
Photoelectric sensors mainly have three common working types: Diffuse Reflective, Specular Reflective, and Through-Beam. Each type has different working principles and application scenarios, catering to various industrial needs.
Photoelectric Sensors Diffuse Reflective Type
1️⃣ Working Principle: The emitter and receiver are integrated into the same probe and rely on diffuse reflection (Lambertian reflection) from the object's surface. After the light is scattered by the object, a portion returns to the receiver, triggering the signal.
2️⃣ Applicable Scenarios:
▪️Object Characteristics: Suitable for non-transparent and rough-surfaced objects (e.g., cardboard, wooden pallets, dark plastics).
▪️Limitations: Prone to misjudgment with highly reflective objects (mirrors/metal), and for black light-absorbing objects (e.g., rubber), detection distance may need to be reduced.
▪️Industrial Cases:
Packaging Lines: Detects the position of cardboard boxes (distance ≤ 1m, installation angle avoids reflective interference).
Robotic Grabbing: Recognizes pallet positions (adjust sensitivity for compatibility with different colors).
▪️Environmental Requirements: Avoid direct sunlight (choose models with anti-light interference, e.g., modulated frequency >5kHz).
Photoelectric Sensors Specular Reflective Type
1️⃣ Working Principle: The emitter and receiver are on the same side, relying on a reflector (prismatic reflector) to return the light along the same path. When an object blocks the light path, it triggers the signal.
2️⃣ Applicable Scenarios:
▪️Object Characteristics: Can detect transparent/semitransparent objects (e.g., glass bottles, PET films), relying on the stability of the reflector.
▪️High Precision Detection: Resolution can reach ±0.1mm (e.g., detecting film tension).
▪️Industrial Cases:
Pharmaceutical Industry: Detects the presence of ampoules (reflectors need to be corrosion-resistant, e.g., 316L stainless steel).
Printing Machines: Detects transparent film breakage (requires polarized filters to eliminate mirror-like interference).
▪️Environmental Requirements: Long-distance detection (up to 50m) requires a laser light source, and dust environments require periodic cleaning of the reflector.
Photoelectric Sensors Through-Beam Type
1️⃣ Working Principle: The emitter and receiver are separated and directly detect light path obstruction. It has the strongest anti-interference capability, as the receiver only recognizes the specific frequency light signal from the emitter.
2️⃣ Applicable Scenarios:
▪️Object Characteristics: Suitable for objects of any material (including transparent/highly reflective), with detection reliability >99.9%.
▪️Micro Object Detection: Fiber-optic through-beam types can detect objects as small as 0.1mm in diameter (e.g., electronic component pins).
▪️Industrial Cases:
Automotive Welding Lines: Detects car bodies passing through (high-temperature models, -25°C~80°C).
Logistics Sorting: High-speed parcel counting (response time <1ms, IP67 protection).
▪️Environmental Requirements: Long distances (up to hundreds of meters) require synchronized signal transmission, and vibration environments require mechanical reinforcement of installation.
How to Choose a Photoelectric Sensor?
1️⃣ Object Detection:
• Transparent/Reflective → Through-Beam or Specular Reflective Type (with polarized filters).
• Black/Light-Absorbing → Diffuse Reflective Type (reduce detection distance or choose a laser light source).
2️⃣ Detection Distance:
• ≤ 0.3m → Diffuse Reflective Type (economical choice).
• 0.3–10m → Specular Reflective Type (requires reflector maintenance).
• 10m → Through-Beam Type (laser light source + synchronized signal).
3️⃣ Environmental Interference:
• Dust/Oil → Through-Beam Type (IP69K protection) or Specular Reflective Type (regular cleaning).
• Strong Ambient Light → Modulated light + narrow-band filtering (e.g., 940nm infrared to resist sunlight interference).
4️⃣ Response Speed:
• High-Speed Production Lines (>1kHz) → Through-Beam Type (fiber-optic type can reach 100kHz).
| Industry | Recommended Type | Typical Case | Technical Key Points |
| Food Packaging | Diffuse + Specular Reflective | Detecting food boxes covered with transparent film | Compensate for film reflection interference |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Through-Beam (Fiber-optic) | Wafer transport positioning | 0.01mm repeatable precision, clean environment |
| Steel Metallurgy | Through-Beam (High-temperature type) | Continuous casting billet position detection | High-temperature resistant (>150°C), anti-electromagnetic interference |
Warehousing & Logistics | Specular Reflective (Long Distance) | AGV navigation using reflective boards | 10–30m detection, multi-reflector encoding |
Engineering Details Often Overlooked
1️⃣ Installation Angle: Diffuse Reflective type should avoid the mirror reflection angle of the object (e.g., metal surfaces should be installed at a 15° angle).
2️⃣ Background Suppression: Advanced diffuse reflective sensors can be programmed to detect objects within specific distances (suppress background interference).
3️⃣ Safety Redundancy: For safety gate applications, Through-Beam types must comply with the EN/IEC 61496-1 standard (dual-channel redundancy).
Photoelectric Sensors
| Ultra-thin Micro GP13 Series | |||
| Type | Model | Detection range | |
Diffuse Reflective | GP13-03N-ZAA | 2~30 mm (White paper) | |
GP13-03P-ZAA | 2~30 mm (White paper) | ||
Through-Beam (Front detection) | GP13-D30N-ZBA | 300 mm | |
GP13-D30P-ZBA | 300 mm | ||
GP13-D50N-ZBA | 500 mm | ||
GP13-D50N-ZBA | 500 mm | ||
Through-Beam (Side detection) | GP13-L30N-ZBA | 300 mm | |
GP13-L30P-ZBA | 300 mm | ||
GP13-L50N-ZBA | 500 mm | ||
GP13-L50P-ZBA | 500 mm | ||
Photoelectric Sensor with Background Suppression Function
What is the Background Suppression Function of a Photoelectric Sensor?
The Background Suppression (BGS) function is a detection technology based on the principle of triangulation. It works by limiting the sensor's effective detection range, making it respond only to objects within the set distance while ignoring background objects. This function is primarily used in diffuse reflective photoelectric sensors but is also applicable to other types, such as specular reflective sensors. Its core feature is the ability to effectively distinguish between target objects and background interference, making it especially suitable for detecting low-reflectivity objects or in complex background environments.
Hot Sales Products
Response time: up to 1.5ms
Repetitive accuracy: up to 10µm
Detection range: 150-3000 mm
Material: plastic accessories, filled with epoxy resin
Connection type: 5-pin M12 connector
Output method: analog voltage 0-10V+PNP
Range: 10mm(±5mm)
Repeat accuracy: < 1μm
Linearity: ±0.4% F.S
Measurement force: min 0.2N
Detection distance: 18 to 28 mm
Power supply voltage: 24 V DC ± 10% pulsation P-P below 10%
Mode switching input: Color pattern or Color mode
Output type: NPN or PNP

















