How Does a Safety Light Curtain Work?
- Share
- publisher
- Vicky
- Issue Time
- Aug 27,2024
Summary
The working principle of the safety light curtain is based on photoelectric sensing technology. In normal operation, the emitter emits infrared beams, which are then received by the light receiver on the opposite side. The controller is responsible for transmitting and converting these optical signals to ensure the stable operation of the entire system.
Light Curtain Sensor Working Principle
The safety light curtain sensor working principle is based on photoelectric sensing technology. In normal operation, the emitter emits infrared beams, which are then received by the light receiver on the opposite side. The controller is responsible for transmitting and converting these optical signals to ensure the stable operation of the entire system. When the light barrier area formed between the emitter and the light receiver is not blocked by any object, the system maintains a stable signal state.
However, when a person or object enters this light barrier area, the situation changes. The blocking or reflection of the infrared beam by the object will cause the light signal received by the light receiver to change. This change is quickly captured by the control system inside the safety light curtain and analyzed and processed. Once the control system detects an abnormality in the light signal, it will immediately trigger an alarm signal and control the relevant mechanical equipment to stop running, thereby effectively avoiding possible accidental injuries.
Basic Components of Safety Light Curtains
Safety light curtains, also known as photoelectric safety protection devices or safety protectors, are mainly composed of light emitters (photoelectric transmitters), light receivers (photoelectric receivers), controllers, and mounting brackets. These components are arranged in a straight line or plane at precise intervals, together forming an invisible light barrier.
Working Modes of Safety Light Curtains
There are two main working modes of safety light curtains: linear scanning and cross scanning. The linear scanning method is relatively simple and suitable for certain specific scenarios; while the cross scanning method is favored due to its higher detection accuracy. Cross scanning forms a denser monitoring network through the intersection of light beams between multiple transmitters and receivers, which can more accurately detect and respond to objects entering the light barrier area.
Application Scenarios of Safety Light Curtains
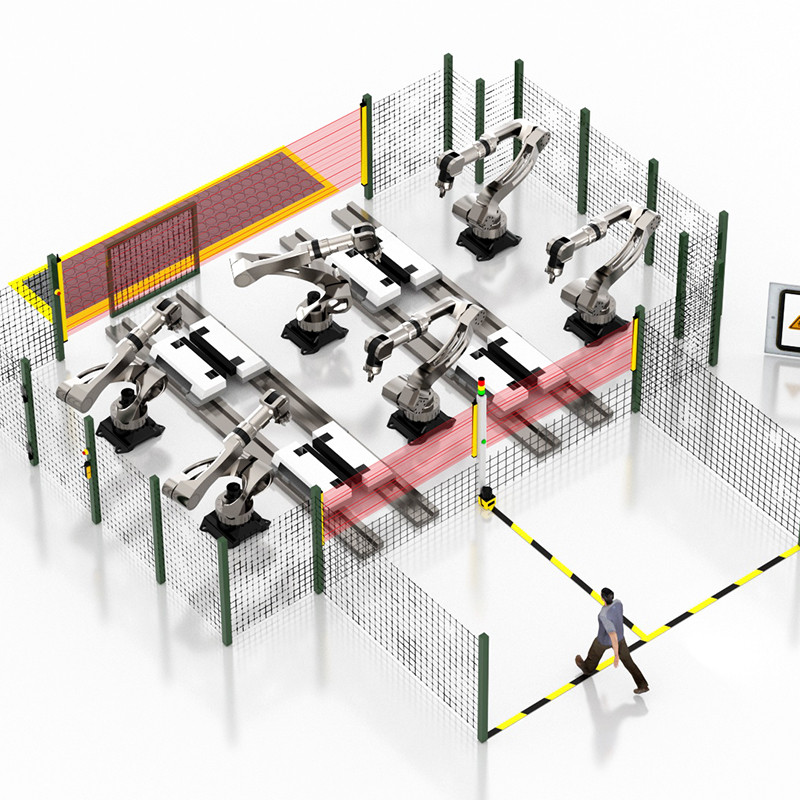
Safety light curtains are widely used, covering almost all industrial fields that require safety protection. In equipment such as elevators, shielding doors, and packaging machinery, safety light curtains can effectively prevent injuries caused by accidental door closures. On potentially dangerous machinery such as stamping equipment, shearing equipment, and metal cutting equipment, safety light curtains can monitor the work area in real time. Once a worker enters a dangerous area, the equipment will be stopped immediately to protect the worker's safety.
Precautions for Safety Light Curtains
1. Ensure that the safety light curtain is firmly fixed on the equipment to be equipped, and the transmitter and receiver are located in the same plane to form an effective protection area.
2. Regularly check the cable connection of the transmitter and receiver to ensure that the cables are accurately and firmly connected to the power supply and control unit.
3. The position of the photoelectric protection device shall not be changed at will to avoid affecting its detection accuracy and stability.
4. When the safety light curtain is blocked in the protection zone, the relevant mechanical equipment should be able to stop running immediately to verify the effectiveness of the safety light curtain.
DADISICK's Hot Selling Safety Light Curtains
Beam spacing:40mm
Number of optical axes:20
Protection height:760mm
Safety sensors for machines output (OSSD):2 PNP
Beam spacing: 10mm
Number of optical axes: 102
Protection height: 1010mm
Safety curtain outputs (OSSD): 2 PNP
Beam spacing: 40mm
Number of optical axes: 32
Protection height: 1240mm
Safety sensors for machines outputs (OSSD)2 PNP
Beam spacing: 10mm
Number of optical axes: 164
Protection height: 1630mm



