How to Make a Safety Light Curtain?
- Share
- publisher
- Vicky
- Issue Time
- Sep 14,2024
Summary
The production of safety light curtains requires comprehensive consideration of electronic circuit design, mechanical structure, signal processing algorithm, safety certification, etc. Through reasonable light curtain design and standardized installation, safety light curtains can effectively protect the safety of operators in industrial environments and improve production efficiency.

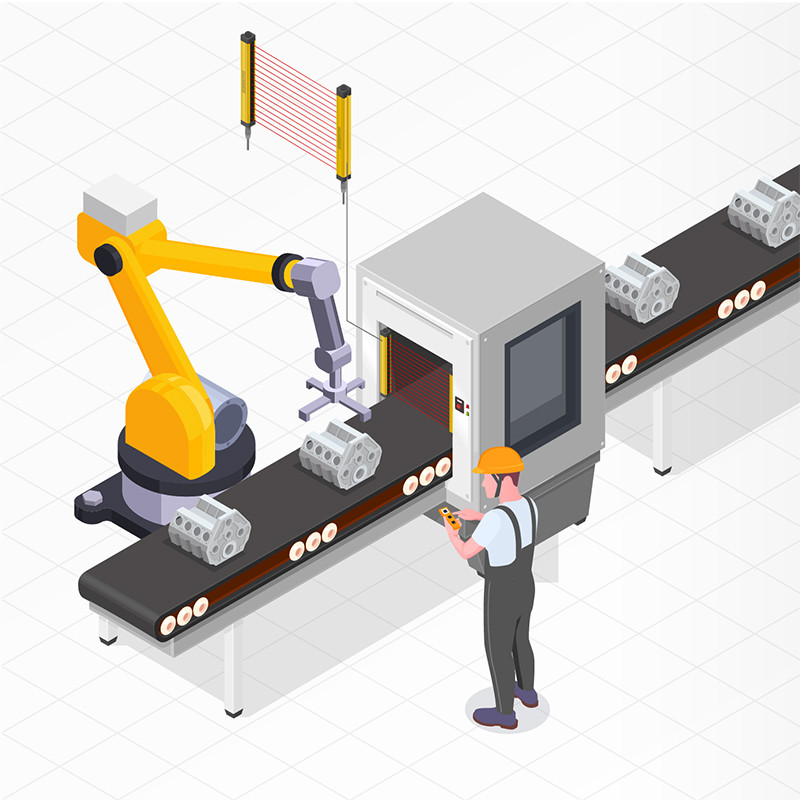
Safety light curtains are important safety protection devices in modern industrial automation, used to prevent people from entering dangerous areas when operating machinery. They emit and receive infrared beams to detect whether objects or people enter the working area, thereby triggering the equipment to stop or take other safety measures. One of the key technical indicators is the safety light curtain resolution, which directly affects the detection accuracy and application scenarios of the equipment.
Understanding How Safety Light Curtain Sensor Working
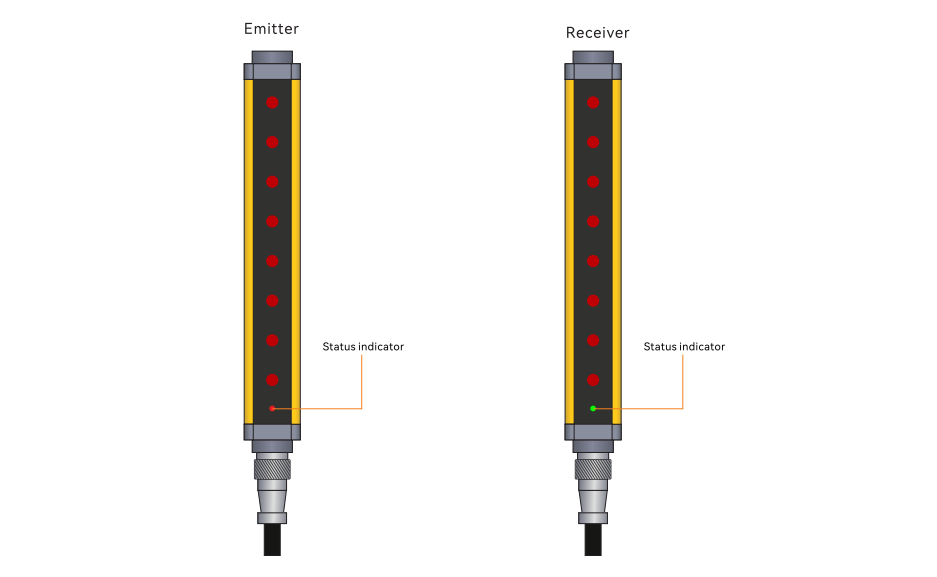
Safety light curtains consist of two parts: a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits a series of infrared beams, and the receiver receives these beams to form a "light grid". When an object or person enters the light curtain area and blocks the beam, the light curtain system will send a signal to trigger the mechanical equipment to stop running, thereby protecting the safety of the operator.
Determine the Light Curtain Resolution and Detection Height
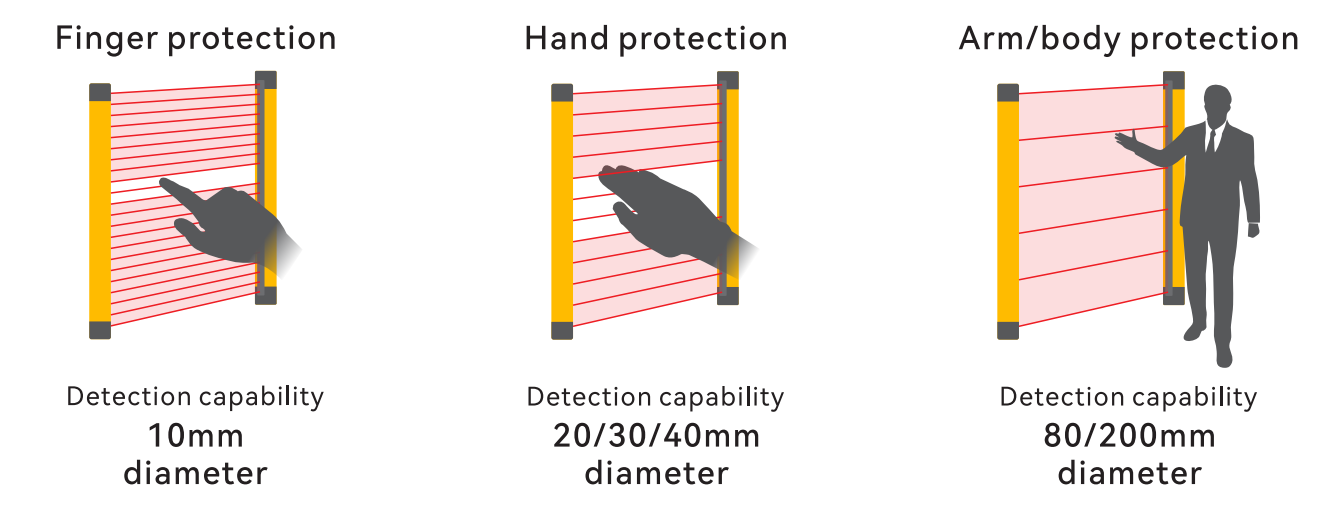
The light curtain resolution determines the smallest object it can detect. Generally speaking, the higher the resolution, the smaller the object the light curtain can detect. The resolution needs to be determined based on the actual application. For hand protection, a resolution of 14-30mm is usually used; for larger objects, such as body protection, the resolution can be relaxed to more than 30mm.
Meanwhile, the detection height refers to the vertical height covered by the light curtain. This usually depends on the size of the equipment or work area to be protected. The appropriate detection height can usually be achieved by adjusting the number and spacing of beams.
Design Electronic Circuit of Safety Light Curtain
The core of the safety light curtain is the electronic circuit, including the design of the transmitter and receiver. Here are some key design considerations:
Transmitter circuit design
The transmitter needs to use infrared LEDs to emit infrared beams. Each LED should be modulated at a certain frequency to reduce interference and ensure signal stability.
Receiver circuit design
The receiver should be equipped with a photosensitive sensor (such as a photodiode or phototransistor) to detect the presence or absence of infrared light. When the receiver does not receive the beam, it sends a signal to the control system to trigger the safety action of the equipment.
Signal processing
The signal processing circuit is responsible for determining whether an object enters the protection area. This can be done with a microcontroller or a dedicated chip. The program needs to monitor the interruption of the signal in real time and trigger the corresponding safety measures.
Building a Solid Safety Light Curtain Mechanical Structure
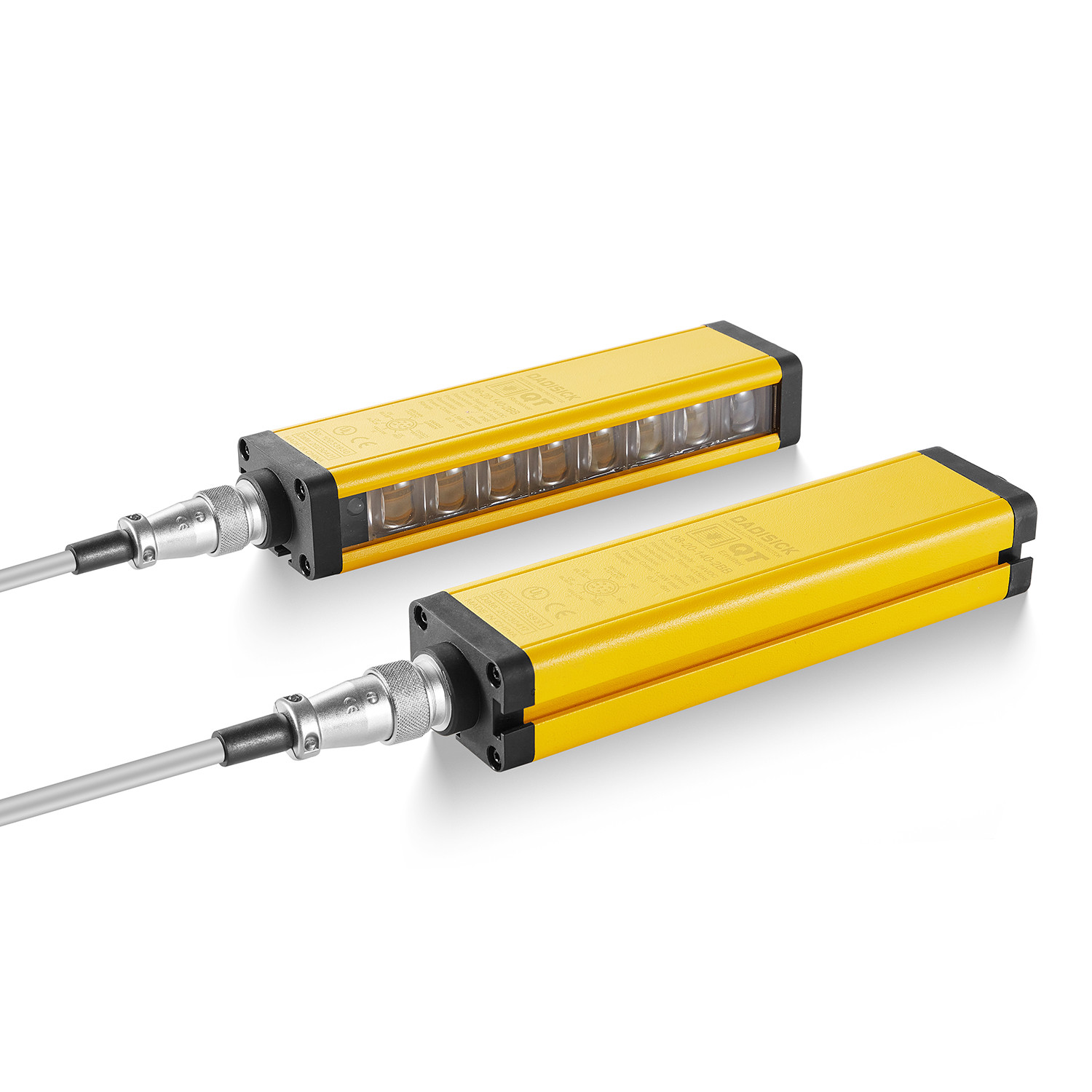

In order to be used in harsh industrial environments, the housing of the safety light curtain must be strong and durable, usually made of aluminum alloy or stainless steel. The mechanical design must ensure that the housing can protect the internal electronic components from shock, vibration and dust, and at the same time be easy to install and maintain.
Safety Light Curtain Software Programming Algorithm
The software part is mainly used for signal processing and control. The program should be able to react at the moment the beam is blocked and issue a stop or slowdown command to the machine. The algorithm needs to ensure that the equipment can respond immediately and safely in abnormal situations (such as misoperation or equipment failure).
In addition, the software should also support parameter setting and real-time monitoring, such as adjusting the detection sensitivity and calibrating the parallelism of the beam.
Safety Certification of Safety Light Curtains

When manufacturing safety light curtains, international and national safety standards must be followed. Common safety standards include ISO 13849-1, IEC 61496-1/2, etc. These standards specify the reliability, redundant design, and fault protection requirements of safety light curtains.
Redundant design
To improve safety, safety light curtains usually adopt dual-channel redundant design. Even if one channel fails, the other channel can continue to work to ensure system safety.
Self-diagnosis function
Safety light curtains should have self-diagnosis function, which can detect whether the system is working properly in real time. If abnormality is found, the system should sound an alarm and cut off the operation of the equipment.
Testing and Calibration of Safety Light Curtains
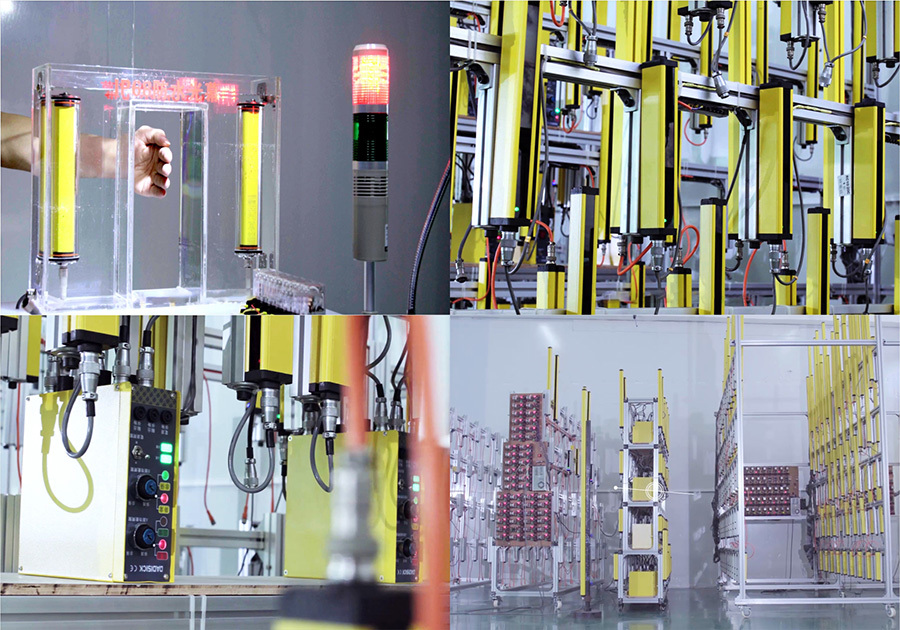
After production, the safety light curtain needs to undergo a series of rigorous tests, including:
Functional test
Ensure that each light beam can work properly and that blocking the beam can quickly trigger the device to shut down.
Response time test
Check whether the system response time meets safety standards, usually requiring a response within a few milliseconds.
Anti-interference test
Ensure that the system can work in a complex industrial environment and is not affected by other light sources or electromagnetic interference.
In addition, the light curtain needs to be calibrated on site to ensure that its transmitter and receiver are fully aligned to avoid misjudgment.
Installation and Maintenance of Safety Light Curtains
When installing a safety light curtain, you must ensure that it fits seamlessly into the protected area and that the installation height is suitable for workers to operate. Regular maintenance and inspections are also very important to ensure that the light curtain's beam is not affected by dust or other obstacles.
DADISICK's Hot Selling Safety Light Curtains
Beam spacing: 2.5mm
Number of optical axes: 32
Protection height: 77.5mm
Beam spacing: 80mm
Number of optical axes: 50
Protection height: 3920mm
Safety Curtain outputs (OSSD):2 PNP
Beam spacing: 40mm
Number of optical axes: 32
Protection height: 1240mm
Safety sensors for machines outputs (OSSD)2 PNP
Beam spacing:40mm
Number of optical axes: 54
Protection height: 2120mm
Safety Curtain outputs (OSSD):2 PNP



