Laser Displacement Sensors Empower SMT Machines: Achieving High-Precision Positioning and Intelligent Quality Control
- Share
- publisher
- Zoe
- Issue Time
- Sep 21,2024
Summary
By integrating laser displacement sensors into SMT machines, a high-precision component positioning and quality monitoring system is created. This solution enables real-time detection of height differences between the PCB and components, automatic correction of positional deviations, and ensures efficient and precise production. It is suitable for assembling high-density electronic components and complex circuit boards, significantly improving production efficiency and product quality.
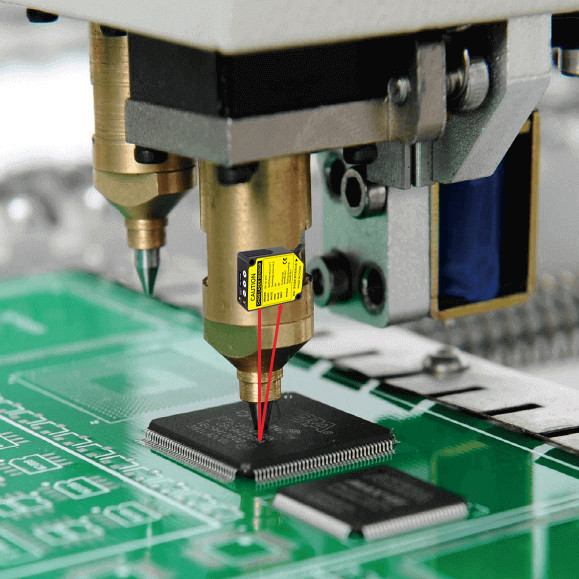
By integrating laser displacement sensors into SMT machines, a high-precision component positioning and quality monitoring system is created. This solution enables real-time detection of height differences between the PCB and components, automatic correction of positional deviations, and ensures efficient and precise production. It is particularly suitable for assembling high-density electronic components and complex circuit boards, significantly improving production efficiency and product quality.
What is an SMT Machine?
An SMT machine (Surface Mount Technology machine) is an automated device used to place electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). It plays an essential role in modern electronics manufacturing, utilizing precise surface mount technology (SMT) to facilitate large-scale component assembly, especially for high-density electronics like smartphones and tablets.
The main working process of an SMT machine includes:
• Component Pickup: The machine picks up electronic components from reels or tape feeders.
• Component Positioning: Using built-in optical or vision systems, the machine precisely detects the intended location on the PCB.
• Component Placement: The picked-up components are accurately placed on the PCB pads, ready for soldering.
Modern SMT machines are not only fast but can also handle various sizes and shapes of components, catering to complex manufacturing needs.
Application of Laser Displacement Sensors in SMT Machines
Laser displacement sensors measure the height of the PCB surface and components with high precision, providing real-time data to the SMT machine to ensure accurate placement of each component. This system greatly enhances the automation level of the production line and reduces manual adjustment errors.
1. Accurate Measurement of Component and PCB Surface Height
Laser displacement sensors can detect the height differences between the PCB and components in real-time, ensuring that each component is placed precisely on the designated pad. This is particularly critical when handling miniature components.
2. Automatic Position Correction
By measuring the height and position of the PCB surface, the system can automatically correct any unevenness or misalignment, reducing placement errors and improving the production yield rate.
3. Flatness Detection of Components
Laser displacement sensors can check the flatness of components before placement, ensuring they meet the requirements of the SMT machine. If non-compliant components are detected, the system automatically rejects them, reducing defects in production.
4. Real-time Quality Control and Monitoring
During the entire placement process, laser displacement sensors provide real-time feedback. Operators or the system can adjust parameters based on this data, ensuring high placement quality and reducing the risk of soldering failures due to incorrect component position or height.
Application Case of Laser Displacement Sensors

Description
DADISICK's GFL-G Series laser displacement sensor is integrated near the pick-up head of the SMT machine to directly monitor the relative height and position between the components and the PCB. The laser sensor accurately measures the height difference between the components and the PCB pads, ensuring precise placement of the components during installation. This technology is particularly suitable for the installation of high-precision components, effectively reducing misalignment and height errors.
Advantages of Using Laser Displacement Sensor Systems
✅ Improved Production Accuracy: Laser displacement sensors offer sub-micron precision, minimizing human error and the need for manual adjustments.
✅ Reduced Defect Rate: By detecting and rejecting non-compliant components, the system reduces the number of defective products in the placement process.
✅ Enhanced Production Efficiency: Automated height detection and correction systems speed up the production process, reducing downtime and rework.
✅ High Adaptability: Laser displacement sensors can accommodate various types of PCBs and components, making them suitable for different manufacturing environments.
Displacement Sensor Based on the Triangulation Principle
Laser displacement sensors typically use the triangulation method. This measurement method can achieve nanometer-level precision, making it suitable for high-precision, short-distance measurements. In current industrial robot applications, triangulation is one of the commonly used techniques, with linearity reaching up to 1 micron and resolution up to 0.1 microns. Laser displacement sensors are commonly used to detect geometric quantities such as displacement, flatness, thickness, vibration, distance, and diameter of objects. These sensors play a crucial role in industrial manufacturing, precision machining, and quality control.
Measurement Range: 24 mm to 400 mm
Resolution: Min. 2 μm; Max. 75 μm
Protection Rating: IP64
Supported Interfaces: RS485 / Switch Output / Analog Current and Voltage
Measurement Range: 25 mm to 600 mm
Repeatability: Min. 10 μm, Max; 800 μm
Protection Rating: IP60
Supported Interfaces: RS485 / Switch Output / Analog Current and Voltage
Distance Sensor Based on the Phase-Shift Method
Laser distance sensors usually adopt the pulse method (ToF) or phase-shift method, and due to their suitability for a wider range of distance measurement needs, they are widely used in industrial production automation. These sensors not only meet the requirements for long-distance measurement but also feature high precision and fast response times. In the field of industrial automation, laser distance sensors are extensively used for position control and navigation, contour measurement and surface inspection, safety protection, logistics and warehouse management, as well as automated welding and cutting. They provide reliable distance measurement data for automation systems, helping to improve production efficiency, accuracy, and safety. They also demonstrate unique advantages in emerging fields such as intelligent transportation and autonomous driving.
Measurement Range: 0.1 m to 50 m
Distance Measurement Principle: Phase-Shift Method
Resolution: 1 mm
Protection Rating: IP67
Supported Interfaces: RS485 / Switch Output / Analog Current and Voltage
Measurement Range: 0.2 m to 100 m
Distance Measurement Principle: Phase-Shift Method
Resolution: 1 mm
Protection Rating: IP67
Supported Interfaces: RS232 / RS485 / Switch Output / Analog Current and Voltage



