Versatile Ultrasonic Sensors: Output Options and Applications in Industrial Automation
- Share
- publisher
- Zoe
- Issue Time
- Jul 12,2024
Summary
Ultrasonic sensors exhibit excellent performance in non-contact positioning and distance measurement applications. They are unaffected by color and shape, and are not limited by the material of the target being measured. As a result, they have been widely used in industrial automation scenarios.

Versatile Ultrasonic Sensors: Output Options and Applications in Industrial Automation
Ultrasonic sensors exhibit excellent performance in non-contact positioning and distance measurement applications. They are unaffected by color and shape, and are not limited by the material of the target being measured. As a result, they have been widely used in industrial automation scenarios.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors use the properties of sound waves to provide a non-contact and precise detection solution for measuring the state and distance of objects. The sensor works by emitting high-frequency mechanical sound waves and receiving the sound waves reflected back from the object. By calculating the time or energy between the emitted and received sound waves, it determines the precise distance or state of the target object.
Ultrasonic sensors differ from ordinary proximity switches and photoelectric sensors. Compared to inductive or capacitive proximity switches, they have a longer detection range; compared to photoelectric sensors, they can operate in harsher environments and are not affected by the color of the target object or the presence of dust, mist, etc., in the air. Ultrasonic sensors are suitable for detecting various states of objects, such as liquids, transparent materials, reflective materials, and particulate matter.
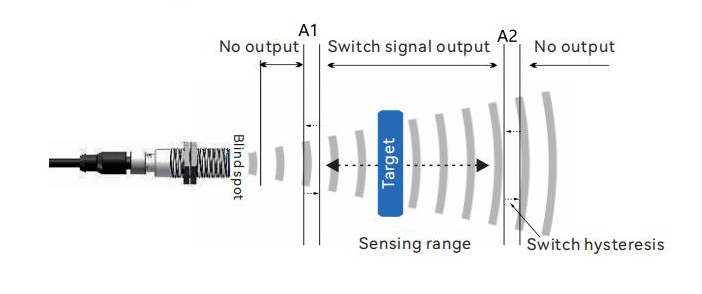
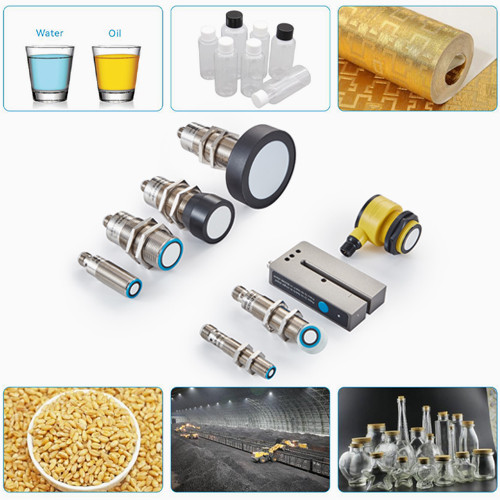
1. Switch output, NO/NC set
3. Digital output: RS485
The sensor is set to Modbus protocol by default from the factory. Custom protocols can be configured according to customer requirements.
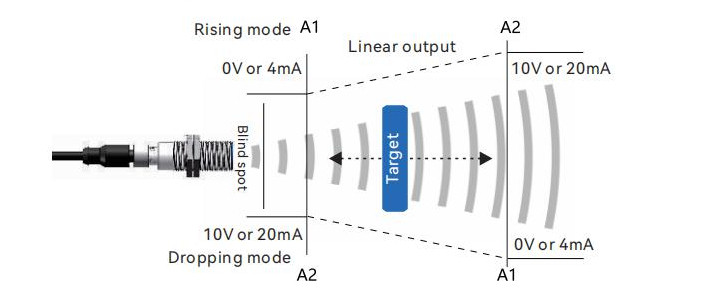
2. Analog output, up/down mode set
The sensor's analog current output type is set to the minimum detection distance value and the maximum detection distance value, which correspond to 4mA and 20mA, respectively.
Both the analog voltage output type and analog current output type can be set to switch to a decline mode by setting the A2 points nearby.
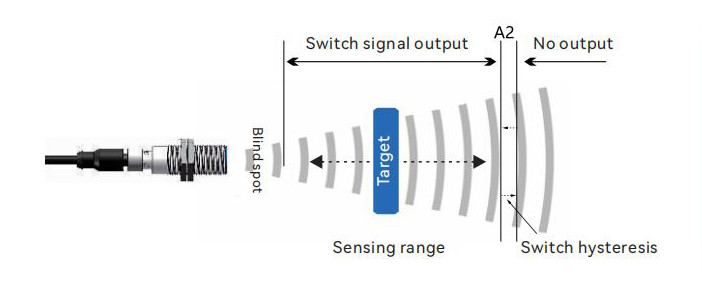
4. Proximity switch mode
The sensor sets an independent switch point, A2. Different outputs are activated when the target passes within the corresponding A2 switch point distance. The switch point can be arbitrarily set within the detection range.
This operating mode is suitable for applications such as counting or presence detection on conveyor belts.
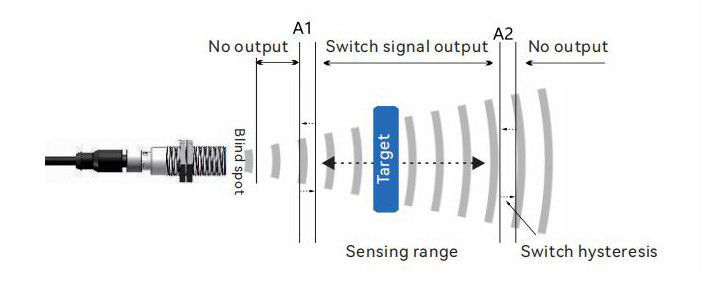
5. Window mode (interval mode)
In window mode, the sensor can set two switch points, A1 and A2. Each output is only activated within the A1 to A2 interval. These two switch points can be arbitrarily set within the detection range.
This operating mode is suitable for applications such as defect rate detection. For example, it can be used to check if bottles inside a wooden crate meet height standards, detecting products that are too tall or too short.
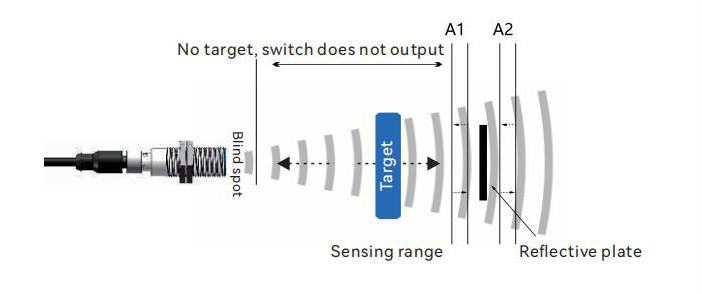
6. Retro-Reflective Mode
The retro-reflective mode is essentially a special window mode where a fixed reflector is placed within the set window. The sensor will emit a signal as long as the target object completely obstructs the reflector.
This operating mode is similar to photoelectric retro-reflective sensors. Ultrasonic sensors do not require a dedicated reflector; any reflective object can be used, regardless of whether the target absorbs or redirects sound waves. This mode can be used to detect foam or other sound-absorbing materials.
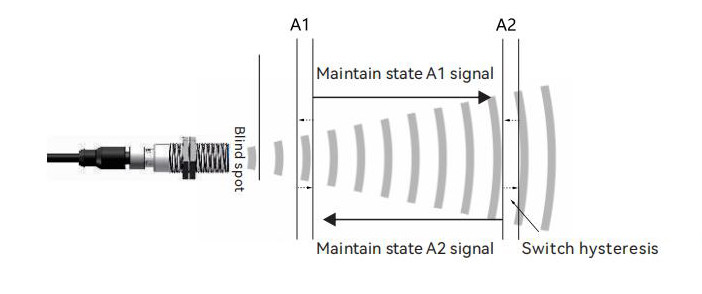
7. Dual-Switch Mode (Hysteresis Mode)
The sensor sets points A1 and A2 within the detection range. When the target reaches point A1 or A2, the output switches. As the target moves from A1 (A2) to A2 (A1), the sensor maintains the current switch state. The output switches back to the original state only when the target passes point A2 (A1).
This operating mode is used for automatic control of liquid levels and material levels.
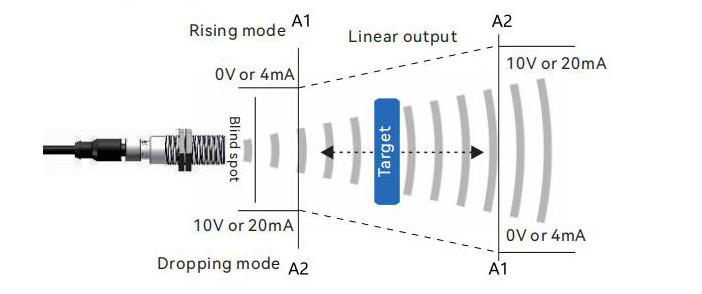
8. Analog Output Mode
Within the effective detection range, the sensor can arbitrarily set points A1 and A2. The distance value between points A1 and A2 is proportionally output as a voltage (0-10V) or current (4-20mA) signal.
The distance information of the target object is output linearly and in real-time as an analog signal. Depending on the positions of the A1 and A2 points, the sensor can switch between ascending mode and descending mode.
This operating mode is suitable for various real-time control applications, such as PLCs and frequency converters.
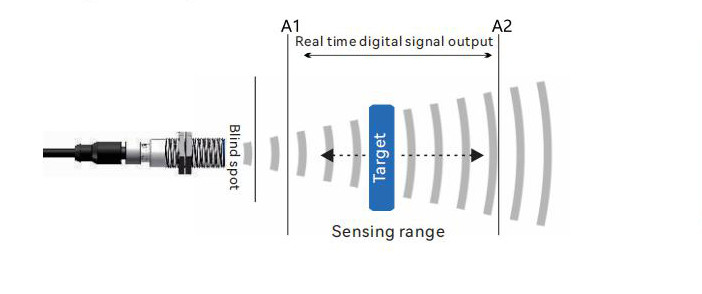
9. Digital Output Mode (IO-LINK, RS232, RS485, TTL, CAN, etc.)
The sensor signals can communicate in real-time at different levels of the system architecture. The measured distance values are transmitted to the controller in the form of serial data bits.
This operating mode is suitable for various developed systems.
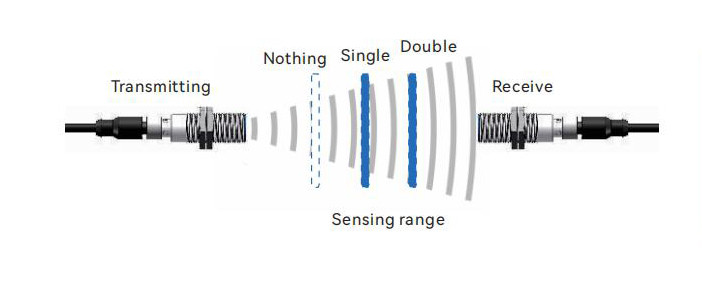
10. Ultrasonic Single and Double Sheet Detection Sensors
Ultrasonic single and double sheet detection operates using a through-beam configuration, assessing the energy of sound waves that pass through varying sheet counts to determine the number of layers. This method is used for detecting single or double sheets of materials such as paper, film, plastic sheets, and metal foils.
Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors exhibit excellent performance in non-contact positioning and distance measurement applications. They are unaffected by color and shape, and are not limited by the material of the target being measured. As a result, they have been widely used in industrial automation scenarios.
🔸Industrial Field: Used for liquid level detection, object detection, distance measurement, and other applications, such as packaging, bottle manufacturing, material handling inspection equipment, and plastic processing.
🔸Automotive Industry: Used for reversing radar, automatic parking, and obstacle detection, enhancing driving safety and convenience.
🔸Biomedical: In the medical field, ultrasonic sensors are used for imaging and diagnosis, such as in ultrasound examinations (B-ultrasound).
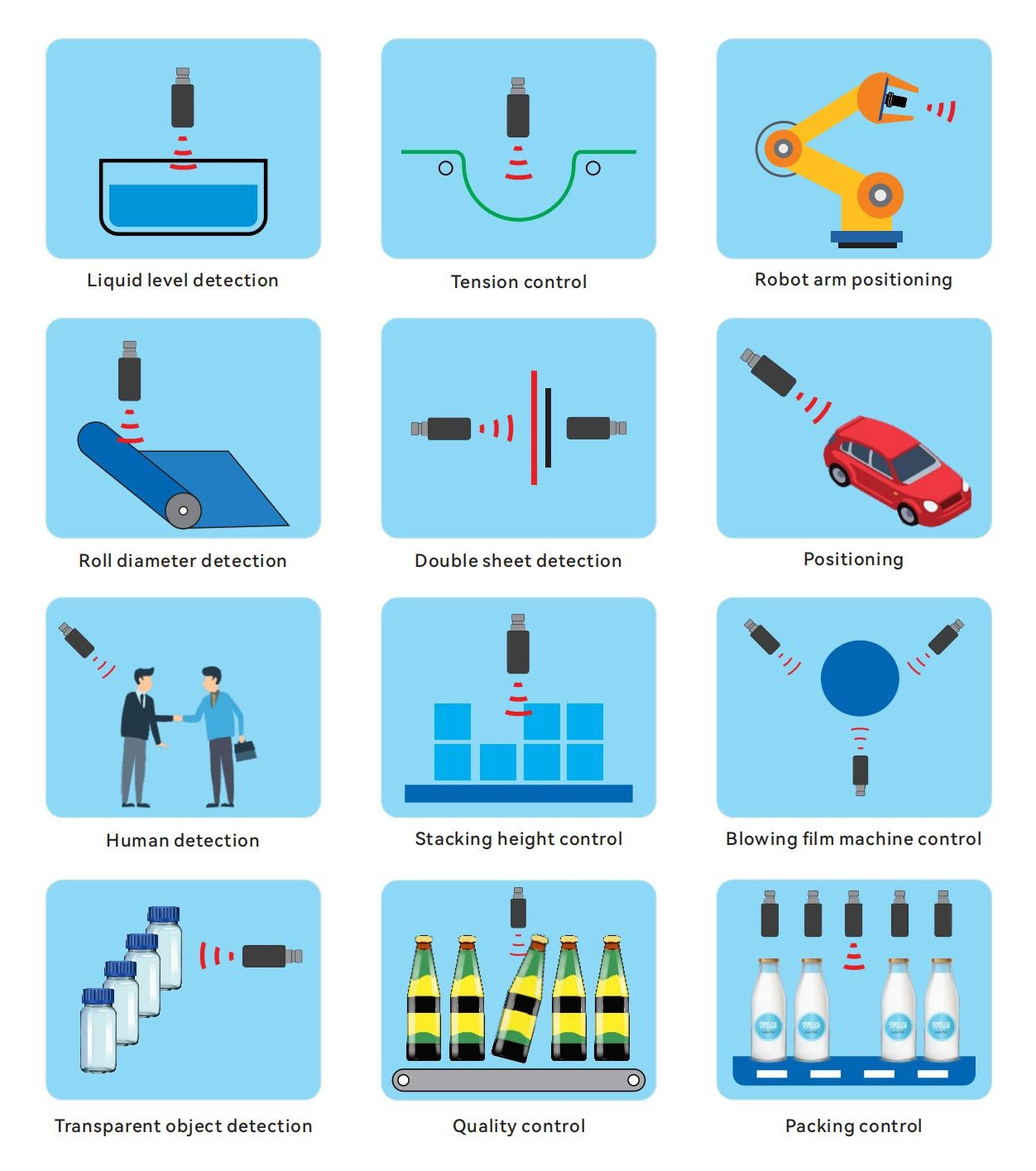
Wide Applications of Ultrasonic Sensors
🔸Liquid Detection: Ultrasonic sensors can detect almost all types of liquids, including pure water, various oils, and various solvents, demonstrating their strong applicability.
🔸Ink and Dye Detection: These sensors can effectively detect inks and dyes of different colors, ensuring precise control in industries such as printing and packaging.
🔸Detection of Transparent and Reflective Materials:
1. Transparent Materials: Ultrasonic sensors can detect a variety of transparent materials, such as glass bottles, glass plates, transparent PP (polypropylene), PE (polyethylene), and PET (polyethylene terephthalate) films, demonstrating their excellent performance in detecting transparent objects.
2. Reflective Materials: They can also detect reflective materials, such as gold foil and silver foil, ensuring accurate operation even in highly reflective environments.
🔸Fiber Fabric Detection: Ultrasonic sensors can easily detect fiber fabrics of various colors, whether dark or light, making them highly applicable in the textile and garment industries.
🔸Automatic Level Control:
1. Solid Materials like Grains: Ultrasonic sensors can be used to detect the level of solid materials like grains, achieving automatic control and monitoring, thus improving storage management efficiency.
2. Powder Level: They are also suitable for the automatic level control of powder materials such as coal, sawdust, and cement, ensuring the stability and safety of the production process.
Highlights of Ultrasonic Sensors
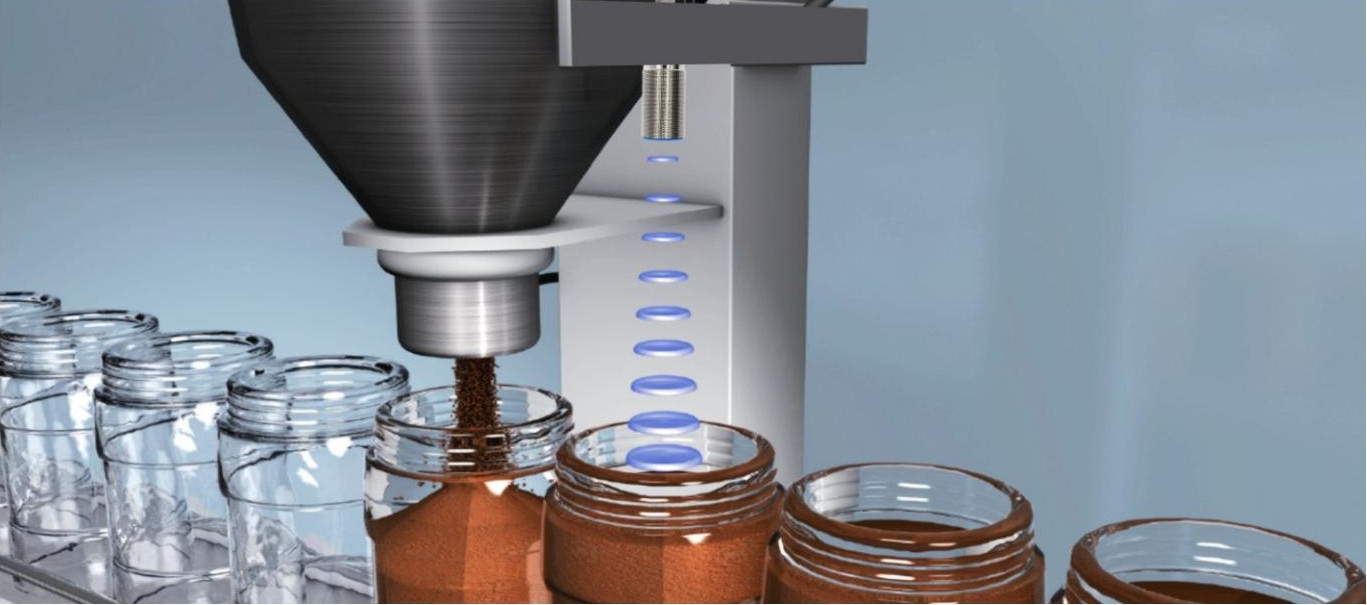
Monitoring Bulk Material Fill Level
Level ultrasonic sensor, ultrasonic sensors are widely used in fields such as industrial automation, warehousing, and logistics. For example, in the warehousing industry, ultrasonic sensors can be used to monitor the material level heights within a warehouse, allowing for timely replenishment of materials or adjustment of storage strategies.
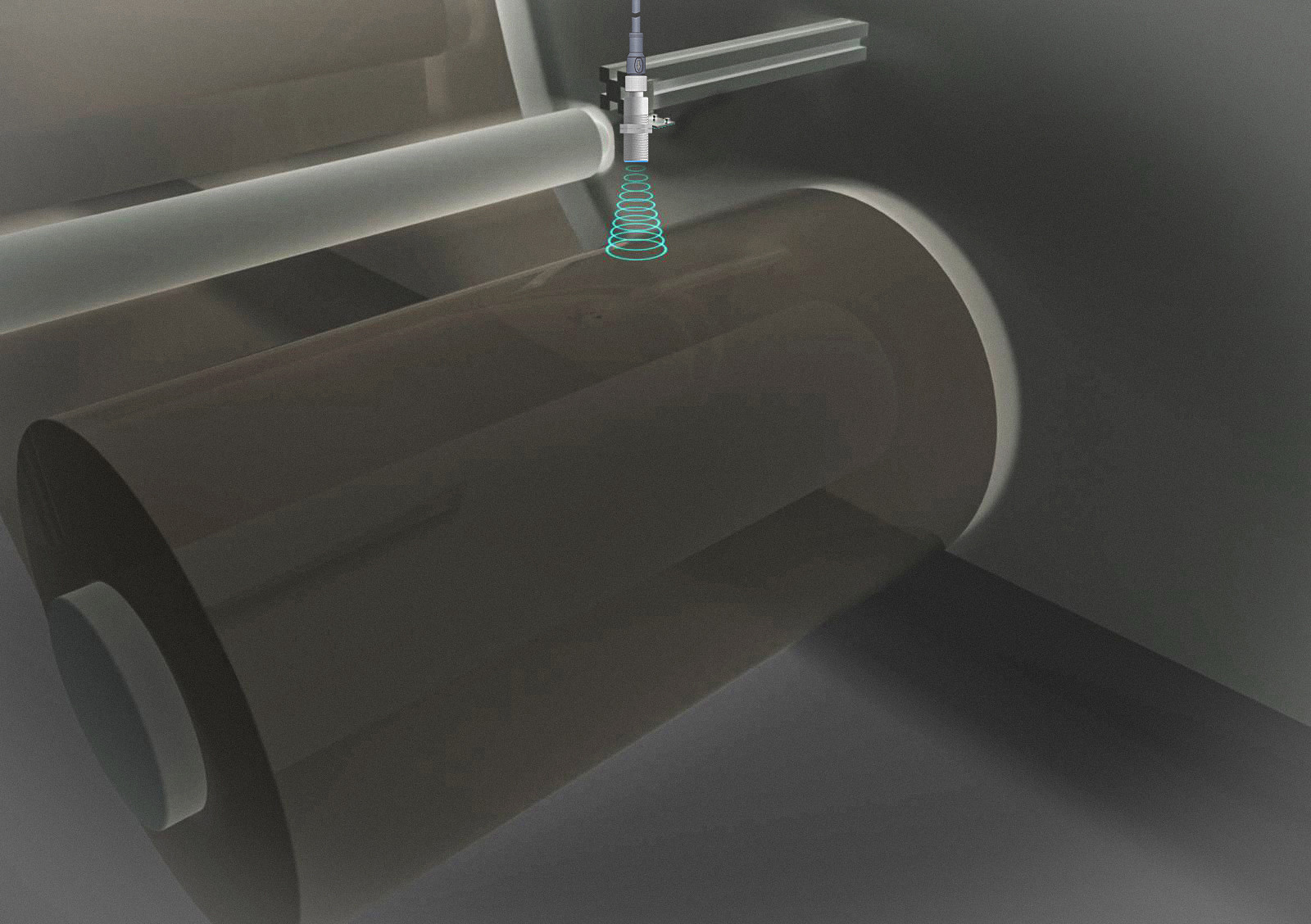


Monitoring Roll Diameter
🔸Basic Principle
An ultrasonic sensor calculates the distance or size of a target object by emitting ultrasonic pulses and receiving the reflected signals. In roll diameter detection, the ultrasonic sensor is installed on the side or above the roll and aligned with the center of the roll shaft. When the pulses hit the roll and reflect back, the sensor calculates the distance to the roll surface based on the echo time and the speed of sound. By combining measurements from multiple points and the geometric characteristics of the roll, the diameter can be determined.
🔸Advantages
1. Non-Contact Measurement: Ultrasonic sensors do not contact the roll surface, avoiding issues of wear and contamination from contact.
2. High Precision: By accurately measuring the propagation time and speed of sound, high-precision roll diameter measurements can be achieved.
3. Strong Anti-Interference Capability: Ultrasonic sensors are less affected by external factors such as light, electromagnetic waves, and dust, allowing them to operate stably in complex environments.
4. Real-Time Capability: Ultrasonic sensors can measure and output roll diameter data in real-time, facilitating timely monitoring and processing by operators.
🔸Application Steps
2. Calibration and Configuration: Calibrate and configure the ultrasonic sensor according to actual needs. This includes setting the sensor's measurement range, triggering mode, output signals, and making adjustments based on the roll material and environmental conditions.
3. Data Acquisition: Start the sensor to begin collecting roll diameter data. The sensor will continuously emit ultrasonic pulses and receive reflected signals, converting the measurement results into a digital output.
4. Data Processing: Monitor the digital output from the ultrasonic sensor via a computer or human-machine interface and map it to the roll diameter. Use linear scaling or other algorithms to calculate the current real-time roll diameter.
5. Monitoring and Alarming: Set up monitoring systems and alarm mechanisms as needed. When the roll diameter reaches a preset threshold, the system will trigger an alarm to alert operators to replace or handle the roll promptly.
High-Performance Compact Ultrasonic Sensors for Demanding Applications
Ultrasonic sensors of various sizes, detection ranges, and output modes offer high flexibility to suit your applications.

|
Models |
CSB12-120
|
CSB12-200 |
CSB18-300 |
CSB18-500 | CSB18-1000 | CSC18-1000 | CSC30-2500 |
|
Detection range
|
20 - 120 mm |
20 - 200 mm
|
30 - 300 mm |
50 - 500 mm | 60 - 1000 mm | 60 - 1000 mm | 150 - 2500 mm |
|
Blind zone
|
0 - 20 mm
|
0 - 20 mm
|
0-30 mm |
0-50 mm | 0-60 mm | 0-60 mm | 0-150 mm |
|
Switching frequency
|
55 Hz
|
45 Hz
|
45 Hz
|
31 Hz | 19 Hz | — | |
Response time | 18 ms | 22 ms | 22 ms | 32 ms | 52 ms | 120 ms | 160 ms |
Hysteresis | 1 mm | 2 mm | — | ||||
Connection type | M12 (4-pin) | M12 (5-pin) | M12 (5-pin) | ||||

|
Models
|
CSB30-2000
|
CSB30-4000 | CSB30-6000 | CSR30-2000 | CSR30-3000 |
|
Detection range
|
100 - 2000 mm
|
200 - 4000 mm | 350 - 6000 mm | 100 - 2000 mm | 150 - 3000 mm |
|
Blind zone
|
0-100 mm |
0-200 mm | 0-350 mm | 0-100 mm | 0-150 mm |
|
Switching frequency
|
10 Hz |
5 Hz | 4 Hz | 10 Hz | 9 Hz |
Response time | 82 ms | 162 ms | 232 ms | 82 ms | 102 ms |
Hysteresis | ±2 mm | ±4 mm | ±5 mm | ±2 mm | ±3 mm |
Connection type | M12 (5-pin) | M12 (5-pin) | |||
|
Models
|
CSDB series
|
Models |
CSDA12-40
|
CSDA18-60 |
CSDA30-100
|
|
Groove depth
|
68 mm |
Detection range |
20 - 40 mm
|
20 - 60 mm |
20 - 100 mm
|
|
Slot width
|
5 mm
|
Blind zone |
5 mm in front
|
7 mm in front |
7 mm in front |
Connection type | M8 (4-pin) | Connection type | 2 m, PVP cable, 0.14 mm² | ||
Unstable Scenarios for Ultrasonic Sensors
To ensure stable and effective operation of ultrasonic sensors, please consider the following situations before testing:
🔸The surface temperature of the target object is higher than 100°C.
🔸The detection environment has wind speeds greater than 60 km/h.
🔸The usage environment is at altitudes exceeding 3000 meters.
🔸In sealed environments where the pressure exceeds 1.2 standard atmospheres.
🔸The operating environment is below -20°C or above 70°C.
🔸In non-reflector mode, detecting materials with high sound absorption, such as felt, wool, cotton, or sponge foam.
🔸Sound waves cannot propagate in a vacuum. Ultrasonic sensors will fail in vacuum environments.
🔸Detecting other unknown substances and uncertain usage scenarios.
Therefore, DADISICK's ultrasonic sensors have made as many compensations as possible in the circuitry to account for various influencing factors, such as temperature drift compensation circuits across the entire series.