How to Choose a Safety Relay: Dadisick's Ultimate Guide
- Share
- Issue Time
- Jul 1,2025
Summary
Discover Dadisick's Ultimate Guide to choosing the right safety relay for your industrial applications. Learn about key selection steps, safety standards like ISO 13849-1 & IEC 62061, and explore our range of safety relays tailored for high-safety monitoring. Enhance personnel and equipment protection with Dadisick's certified safety relays.
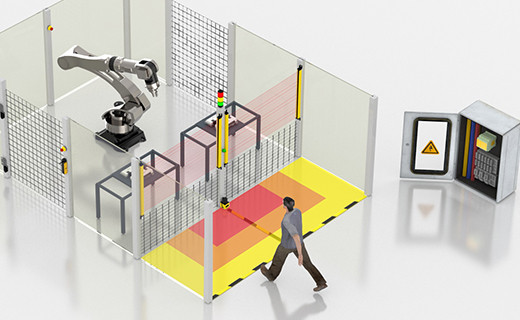
Safety relays are critical components in industrial automation systems, designed to protect personnel and equipment by monitoring and controlling safety functions. Unlike standard relays, safety relays feature redundant and self-monitoring circuits that detect faults in input/output devices and internal circuits, cutting off power to loads and preventing unexpected restarts in hazardous situations. They are widely used in applications such as emergency stops, safety gate monitoring, light curtain control, and two-hand control.
For example, in a robotic packaging unit, safety relays can monitor safety gate switches and emergency stop buttons to ensure the robot stops immediately when an operator enters a hazardous area.
Understanding Safety Standards
Selecting the right safety relay requires understanding relevant safety standards. Two primary standards guide this process. Before selecting a safety relay, perform a formal risk assessment using standards such as ISO 12100, ISO 13849-1, and IEC 62061. Key elements to assess include the severity of possible injury, frequency and duration of exposure, and the possibility of avoiding the hazard. The outcome defines the required Performance Level (PL) rating for each safety function.
ISO 13849-1
Defines Performance Levels (PL) from PLa (low risk) to PLe (high risk), assessing the reliability of safety-related control systems based on severity, frequency of exposure, and the possibility of avoiding hazards.
| Risk Level | PL Rating |
| Low | PLa/PLb |
| Medium | PLc |
| High | PLd |
Very High | PLe |
IEC 62061
Defines Safety Integrity Levels (SIL) for evaluating the risk reduction capability of functional safety systems.
| Safety Integrity Level (SIL) | Probability of Dangerous Failure on Demand (PFDavg) | Probability of Dangerous Failure per Hour (PFH) |
| SIL 1 | ≥ 10⁻² to < 10⁻¹ | ≥ 10⁻⁸ to < 10⁻⁷ |
SIL 2 | ≥ 10⁻³ to < 10⁻² | ≥ 10⁻⁸ to < 10⁻⁷ |
| SIL 3 | ≥ 10⁻⁴ to < 10⁻³ | ≥ 10⁻⁷ to < 10⁻⁶ |
| SIL 4 | ≥ 10⁻⁵ to < 10⁻⁴ | ≥ 10⁻⁶ to < 10⁻⁵ |
These standards help determine the required safety level through risk assessment. For instance, high-risk machinery like heavy stamping presses may require PLe-rated safety relays, while low-risk applications might only need PLa.
Selecting the appropriate safety relay involves a systematic approach. Below are the five key steps:
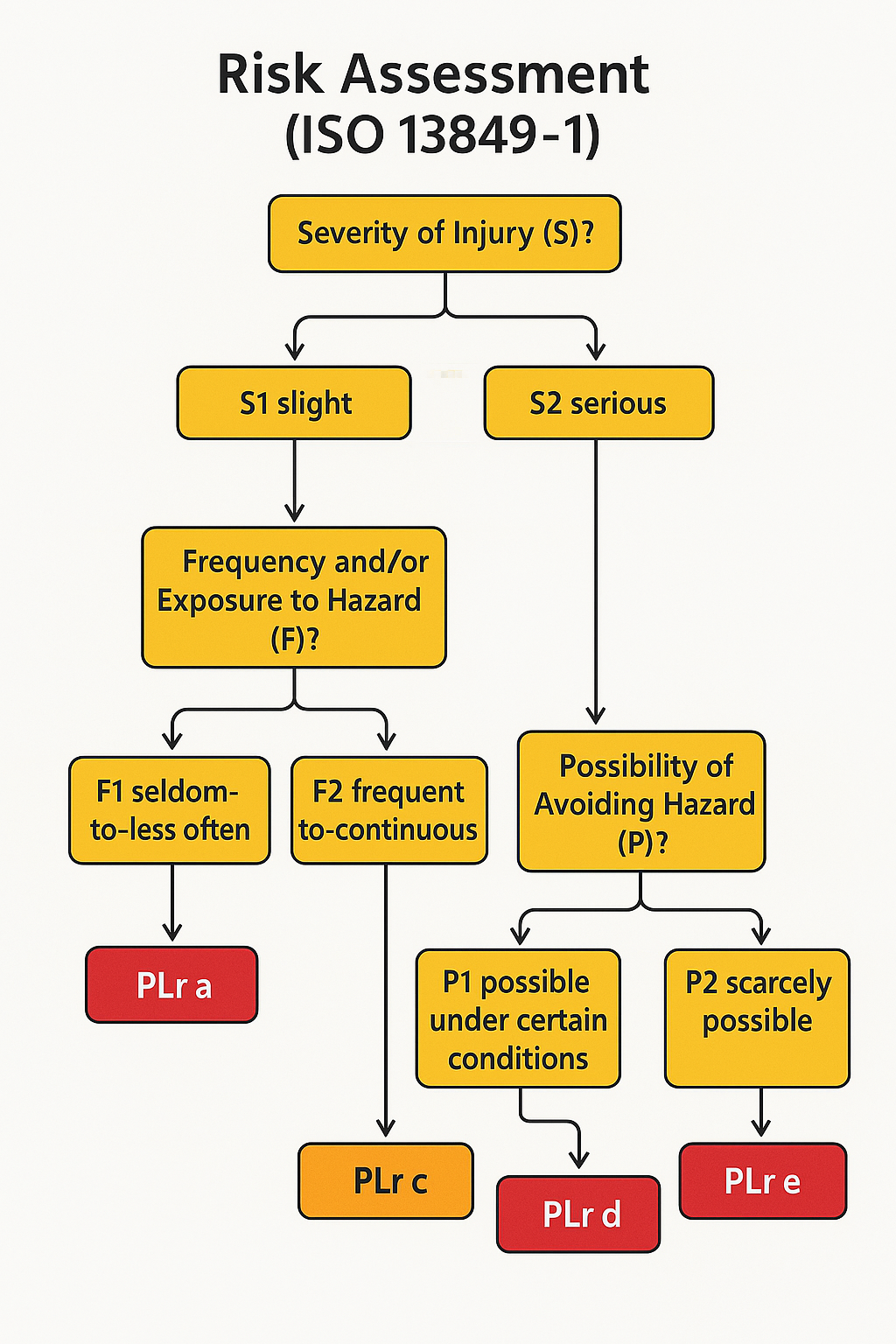
Step 1: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the foundation of choosing a safety relay. Using standards like ISO 12100 or ISO 13849-1, evaluate:
● Severity (S): The seriousness of potential injuries.
● Frequency and duration of exposure (F): How often personnel are exposed to the hazard.
● Possibility of avoiding the hazard (P): The ability of operators to avoid the hazard.
A risk graph determines the required Performance Level (PLr), ranging from PLa (low risk) to PLe (high risk).
Step 2: Determine the Safety Functions
Determine which machine operations need to be controlled or stopped during unsafe conditions. Each function may require a separate safety relay or a multi-channel relay, depending on complexity. Based on the risk assessment, identify necessary safety functions, such as:
● Emergency stop (E-stop)
● Safety gate monitoring
● Two-hand control
● Light curtain or laser scanner monitoring
● Safe speed monitoring
Each function may require specific types of safety relays. For example, an emergency stop might need a dual-channel relay, while light curtain monitoring may require a module supporting multiple inputs.
Step 3: Select the Appropriate Safety Relay
Use the PLr as your benchmark to select a relay capable of achieving or exceeding the required rating. Consider factors such as input type, number of channels, reset mode, reaction time, diagnostic capabilities, and expandability. Consider these key criteria:
| Selection Criteria | Description | |
| PLr Compliance | Ensure the relay meets or exceeds the required Performance Level (PLa to PLe). | |
| Input Types | Match the relay to input devices, such as E-stop buttons or safety switches. | |
| Number of Channels | Choose single, dual, or triple channels based on redundancy needs. | |
Reset Mode | Select manual, automatic, or monitored reset depending on the application. | |
Response Time | Ensure the relay’s response time meets the hazard’s stopping time requirements. | |
Diagnostic Features | Opt for relays with fault detection and LED indicators for easier maintenance. | |
Expandability | Consider if the relay supports additional safety inputs or network integration. | |
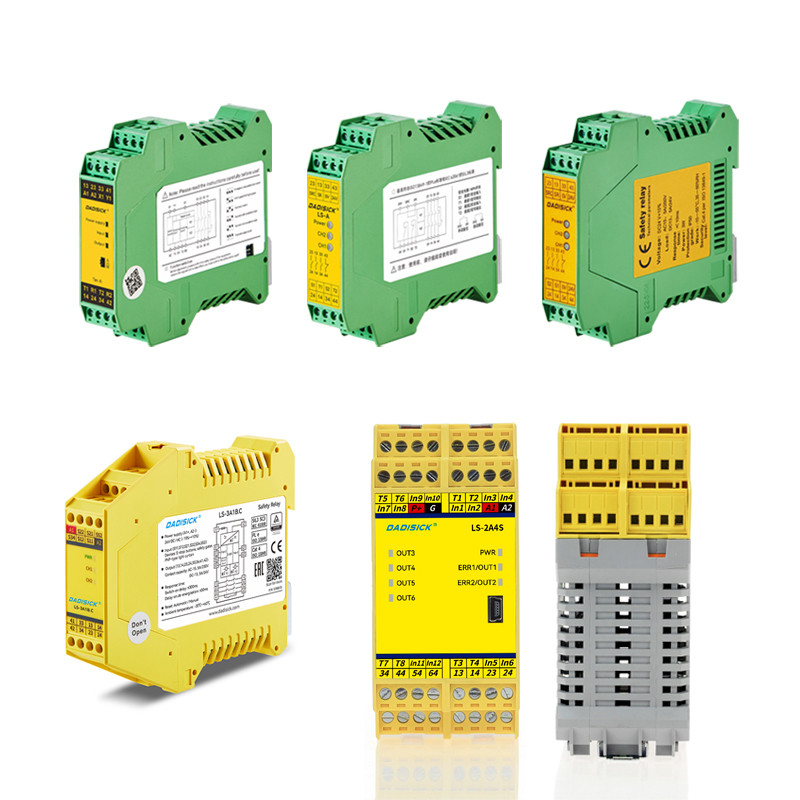

Dadisick offers a range of safety relays tailored to various applications:
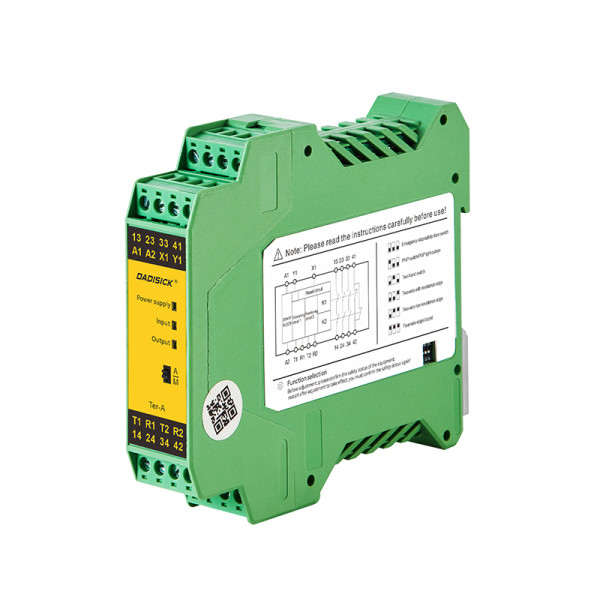
● Ter-A: Multifunctional relay with auto/manual reset and DIP switch configuration, ideal for high-safety monitoring applications.
● LS-A: Economical dual-channel relay suitable for automated production lines and robotic systems.
● LS-3A1B.C: Designed for emergency stops and safety gates, featuring 3 normally open (NO) and 1 normally closed (NC) contacts, cost-effective.
● LS-2A4S: Configurable module supporting 6 safety inputs and multiple outputs, perfect for complex safety systems.
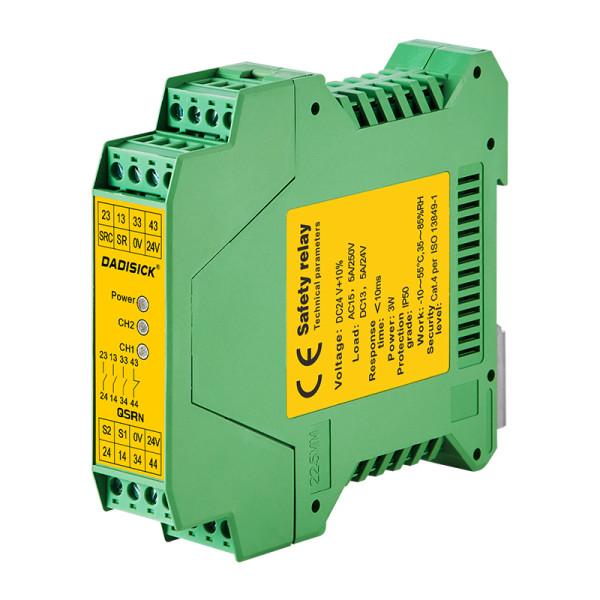
● QSRN: Complies with EN/ISO13849-1 Cat.4, suitable for emergency stops, safety gates, light curtains, and two-hand buttons.
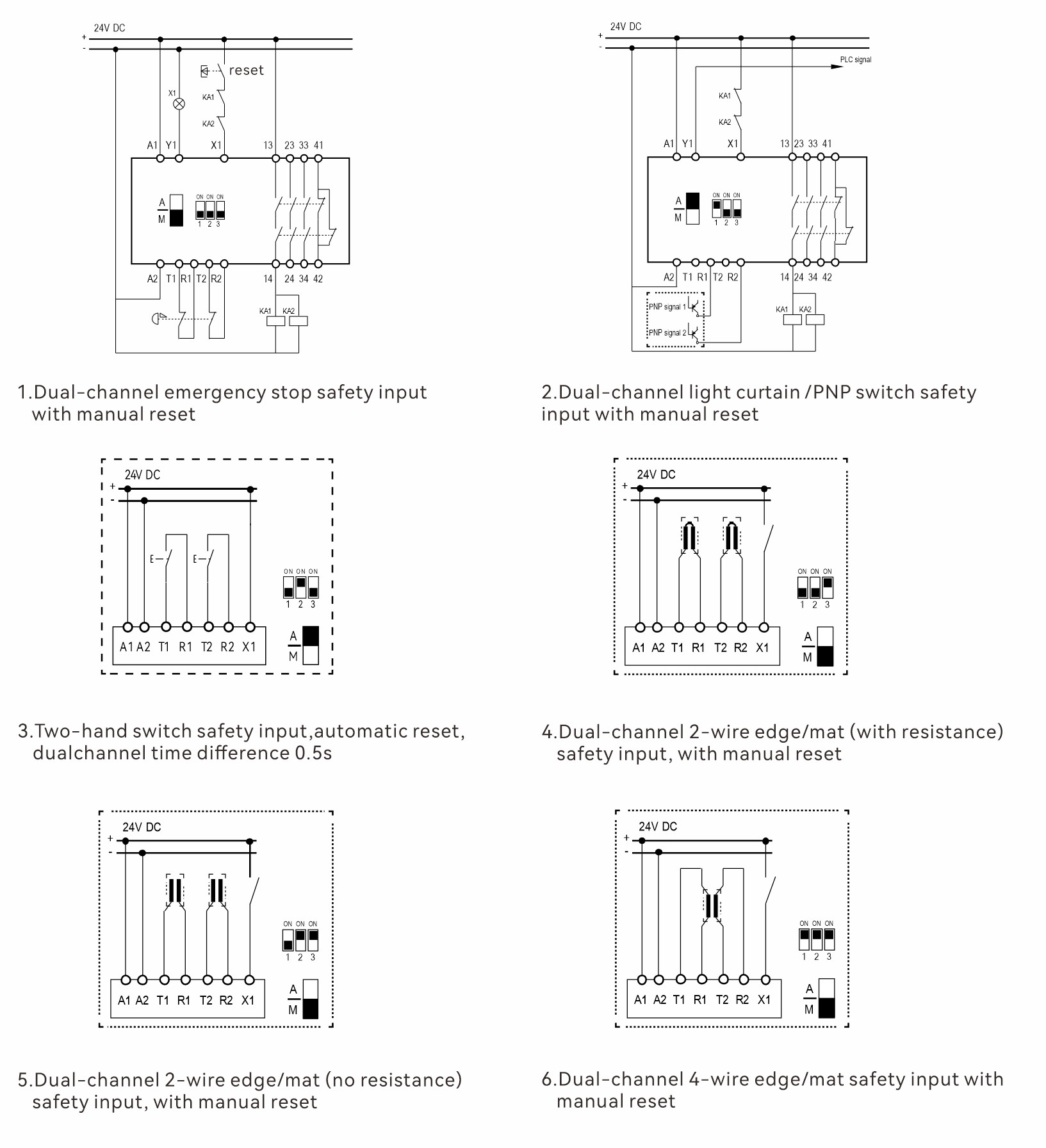
Step 4: Configuration and Wiring
Proper configuration and wiring are essential for a safety relay’s correct operation. Best practices include:
● Using shielded cables to reduce electromagnetic interference.
● Avoiding mixing safety and non-safety circuits.
● nsuring terminals are clearly labeled for easy installation and maintenance.
● Testing outputs to verify functionality.
General Wiring Best Practices:
● Use shielded cables for long-distance inputs.
● Avoid mixing safety and non-safety circuits in the same cable run.
● Ensure adequate spacing in control panels.
● Label all terminals and include them in electrical drawings.
● Test outputs regularly during commissioning.
Dadisick safety relays come with detailed wiring diagrams and configuration instructions, featuring clearly labeled terminals and diagnostic LEDs to simplify installation and troubleshooting. For example, the LS-3A1B.C relay can be easily connected to dual-channel emergency stop buttons and power contactors.
Step 5: Validation and Testing
After installation, validate and test the safety system to ensure compliance with safety standards. The validation process includes:
● Functional Testing: Confirm the relay operates correctly under all expected conditions.
● Fault Simulation: Test the relay’s response to fault conditions.
● Performance Level Verification: Use tools like SISTEMA software to calculate parameters such as B10d, DC, and MTTFd.
Dadisick provides comprehensive documentation and technical support to assist customers in the validation process, ensuring their safety systems are compliant and reliable.
Dadisick is a leading brand in safety solutions, offering a variety of safety relays that meet stringent standards like EN/ISO13849-1 Cat.4 and IEC 62061 SIL3. Their products are designed for reliability, ease of use, and versatility.
| Model | Key Features | Applications | |
Multifunctional, auto/manual reset, DIP switch configuration, high-safety monitoring | Complex industrial systems | ||
Economical, dual-channel design, easy integration | Automated production lines, robotic systems | ||
3 NO + 1 NC contacts, for emergency stops and safety gates | Cost-sensitive applications | ||
Configurable, 6 Redundant channels of safety inputs, multiple outputs | Complex safety systems | ||
Cat.4 compliant, supports multiple safety functions | High-risk industrial environments | ||

Key Features:
● Dual-Channel Design: Monitors transistor or NC switch signals for high reliability.
● Self-Monitoring and Diagnostics: Built-in fault detection with LED indicators.
● Durability: Operates from -25°C to 85°C, with flame-retardant PA66 housing and an electrical life of 80,000 cycles.
● Easy Installation: Compact 22.5mm width, screw or spring terminals, with PLC signal output.
Applications:
● Monitoring emergency stops, safety gate switches, safety light curtains, two-hand buttons, and light curtain signals.
● Protecting operators and equipment in high-safety industrial environments.
Dadisick is committed to providing high-quality safety products and exceptional customer service. Our safety relays are designed to meet the stringent safety requirements of EN/ISO13849-1 Cat.4 and IEC 62061 SIL3. They feature a dual-channel safety monitoring circuit design, capable of monitoring various safety equipment sensor signals. Our safety relays are suitable for high-safety industrial environments, including emergency stop signals, safety door switch signals, safety grating signals, and two-hand button signals. Their advantages include:
● Expertise: Extensive experience in industrial safety solutions.
● Certifications: All safety relays are EN ISO 13849 and CE certified.
● OEM Services: Customization options, including laser marking and tailored solutions.
● Technical Support: Comprehensive support for integration, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
Visit Dadisick's website or contact their sales team for more information or to request a quote.
Conclusion
Selecting and configuring a safety relay is not just about meeting a technical requirement—it’s about protecting lives and ensuring compliance. By starting with a thorough risk assessment, identifying required PL levels, and choosing the right relay for each function, you build a safer and smarter machine.
From E-stop buttons to complex light curtain zones, safety relays form the backbone of risk mitigation in automation. Choose wisely, wire correctly, and always verify your system with international safety standards.
DADISICK offers a wide range of safety relays tailored to meet diverse industrial safety requirements. Our products are designed for reliability, flexibility, and ease of use, making them ideal for various safety applications. Visit DADISICK Safety Relays to explore our product lineup and discover how our solutions can enhance safety in your industrial systems.
Multifunctional safety relay, providing automatic/manual reset configuration and multifunctional configuration DIP switch, used for industrial field monitoring of various signals with high safety requirements.
Economical safety relay, dual-channel safety monitoring circuit design, suitable for high-demand fields such as mechanical protection, automated production lines and robot systems.
LS-3A1B.C is a safety relay suitable for emergency stop, safety door, PNP type safety light curtain signal of various mechanical equipment. It has 3 normally open (NO) safety output contacts and 1 normally closed (NC) auxiliary output contact, and can select single/dual channel operation, manual/automatic reset and short circuit monitoring between channels. It adopts the design of components produced in China, standard housing, convenient wiring and common with mainstream products in the market, with excellent cost performance.
DADISICK LS-2A4S is a configurable safety control module that supports a variety of switch-type safety element inputs (such as emergency stop buttons, safety doors, two-hand buttons, etc.), and supports up to 6 safety element inputs, 2 relay safety outputs, and 4 semiconductor outputs. It can use configuration software to set safety control logic to meet a variety of on-site application requirements.
The QSRN safety relay module meets the safety requirements of EN/ISO13849-1Cat.4 and is suitable for monitoring various signals in industrial sites with high safety requirements – including emergency stop signals, safety door switch signals, safety light barrier signals, and safety light curtain signals. Outside the two-hand button signal.




