Industry knowledge | Small details of using LiDAR sensor in special scenarios
- Share
- Issue Time
- May 29,2024
Summary
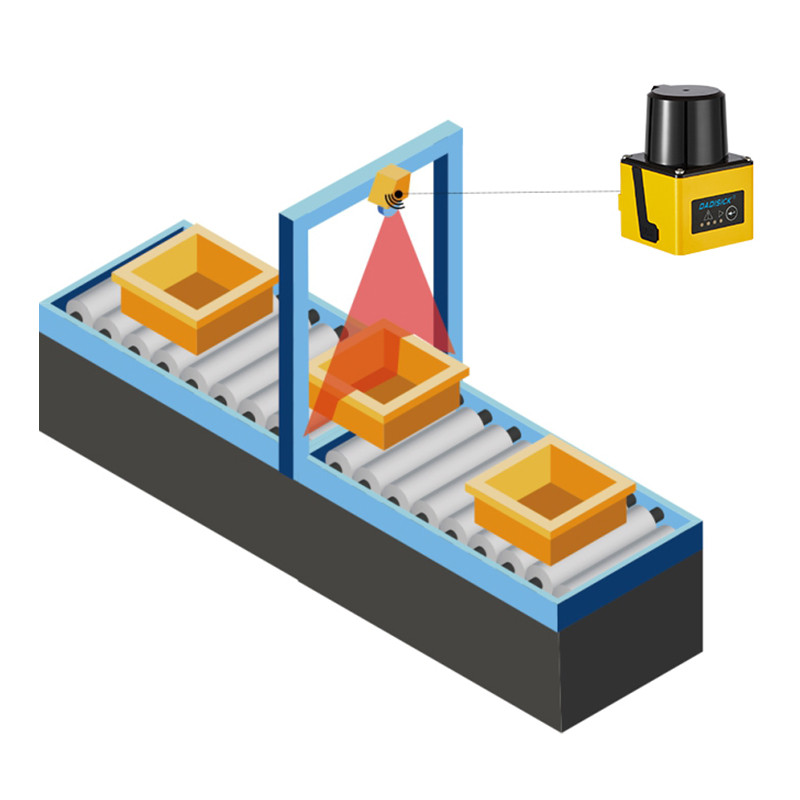
LiDAR sensor products include obstacle avoidance type, navigation type and integrated navigation and obstacle avoidance type; they have the advantages of high measurement accuracy, fast scanning speed, strong anti-interference ability, small size, light weight and high reliability.
LiDAR sensor is a technology first proposed in the 1960s. With its wide application, LiDAR has experienced a new round of prosperity and progress and multi-industry use in the past few years. It has rapidly become a key technology in the fields of autonomous driving, drone inspections, industrial automation, etc.
To date, DADISICK has launched several LiDAR sensor series products, covering obstacle avoidance type, navigation type and integrated navigation and obstacle avoidance type; they have the advantages of high measurement accuracy, fast scanning speed, strong anti-interference ability, small size, light weight and high reliability, and are ideal choices for industrial AGVs, mobile robots and low-speed robots.
Each sensor has its own suitable application scenario based on its own performance characteristics. In actual special environment applications, LiDAR also has some tips for use.
LiDAR sensor working principle
LiDAR sensor is based on the principle of time-of-flight (TOF); LiDAR emits a laser pulse and measures the time it takes for the pulse to return after reflecting from the surface of the target being measured, which is then converted into distance data.
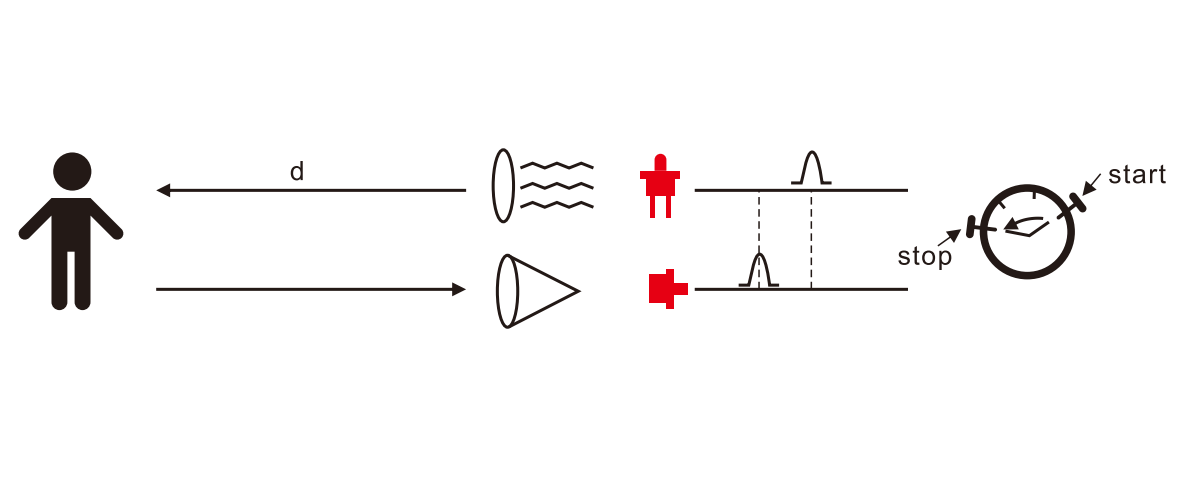
The time difference between emitting light and receiving light is t
c is the speed of light, then the distance between the radar and the target is
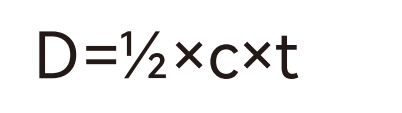
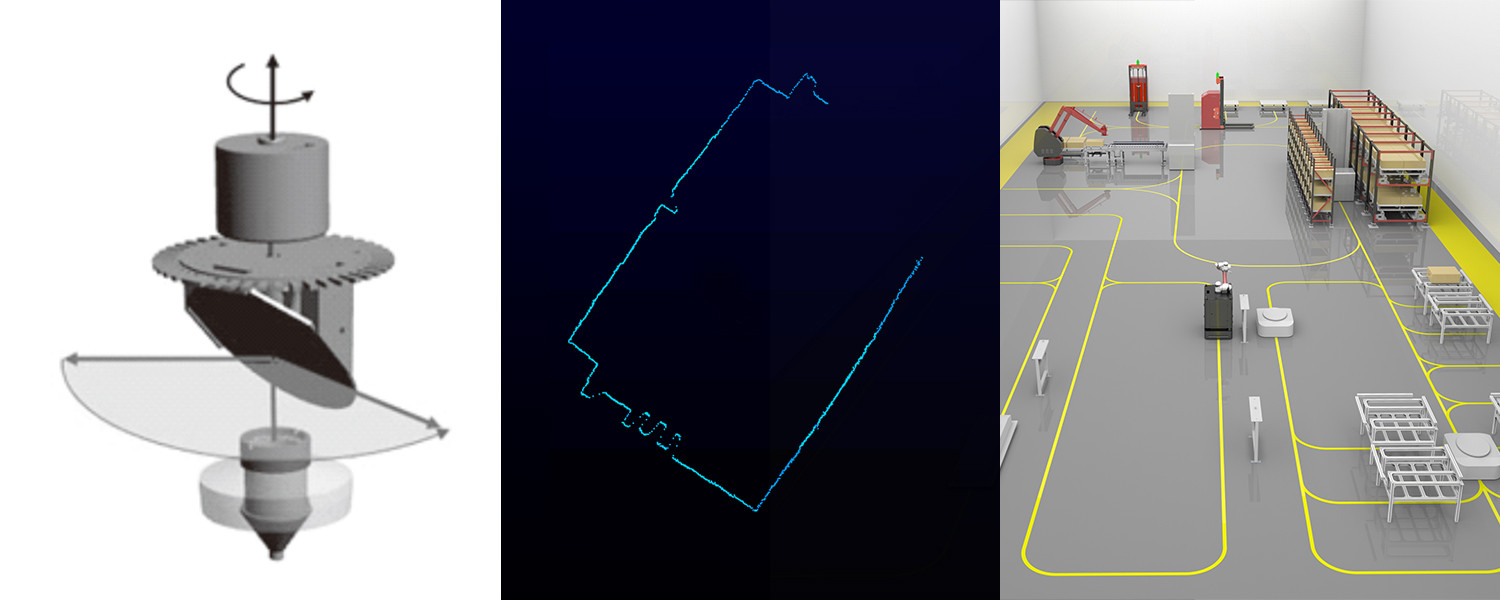
The LiDAR sensor reflects the ranging laser pulse through a reflector. When the reflector is driven by the motor to rotate, a scanning plane perpendicular to the rotation axis is formed. The radar emits pulse light at a fixed time, and the motor drives the transmitting mirror to rotate, so that two-dimensional point cloud data can be formed.
When there is a transparent medium in the surrounding environment
Difficulty:
When there is a transparent medium (such as clean water) in the surrounding environment, the target inside or behind the transparent medium can be measured. Since light will refract in the transparent medium, the measured target is actually located on the refracted light path, while the measurement result is on the straight light path, and the measured target position will deviate. In addition, the radar may also receive two reflected echoes, one from the reflection of the actual target surface inside or behind the transparent medium, and the other from the diffuse reflection of the transparent medium surface that is not completely clean. At this time, the measurement result is uncertain, which may be the medium surface or the actual target.
Countermeasures:
In actual use, transparent media in the environment, especially those with mirror-like surfaces, need special treatment to avoid unstable or erroneous measurement results. The specific treatment method can be to make the surface of the medium diffusely semi-transparent, reduce transparency and reflection ability, or shield these positions when processing measurement data.
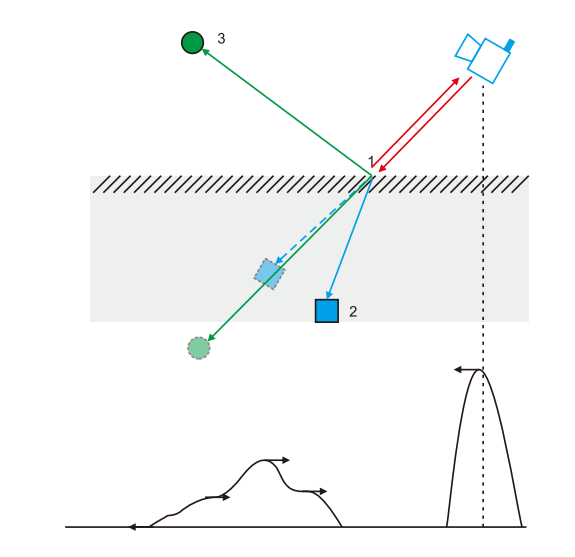
When measuring mirror targets

When the radar measures mirror targets, please pay attention! ! Effective measurement can only be achieved when the target surface is perpendicular to the incident laser. If the laser incident angle is not perpendicular, its diffuse reflectivity is very low, resulting in ineffective measurement. The actual measured result is the mirror target distance on the mirror reflection light path, as shown in the figure:
The radar projection on the mirror target produces total reflection, and the total reflection light is projected on the target. The actual distance tested by the radar is the distance of the dotted frame target.
About the actual range of LiDAR sensor
The actual range of the radar for a specific target will be affected by the following factors:
1. Target diffuse reflectivity:
The target diffuse reflectivity is not only related to the material, but also to the surface orientation. The higher the target diffuse reflectivity, the longer the actual range.
2. Reflection area:
The area of the target surface covered by the laser spot. The larger the coverage area, the longer the actual measurement distance.
3. Dirtiness of the light-transmitting cover:
The dirty light-transmitting cover of the radar will cause the light transmittance to decrease. The more the light transmittance decreases, the worse the measurement capability. When the light transmittance drops to 60%, the measurement capability may be completely ineffective.
4. Atmospheric conditions:
The actual measurement capability of the radar is also affected by atmospheric conditions, especially when working outdoors. The worse the light propagation capability of the atmosphere, the lower the actual measurement capability of the radar. In extreme weather conditions (such as dense fog), the measurement capability will be completely ineffective.
Hot selling products
5m distance, A technique that uses a laser beam to measure distance and create detailed maps of objects and environments.
20m distance, A technique that uses a laser beam to measure distance and create detailed maps of objects and environments.
Sensing range 20m, A technique that uses a laser beam to measure distance and create detailed maps of objects and environments.
By converting from the laser into electrical signals. determine various characteristics,distance, displacement, or position.



