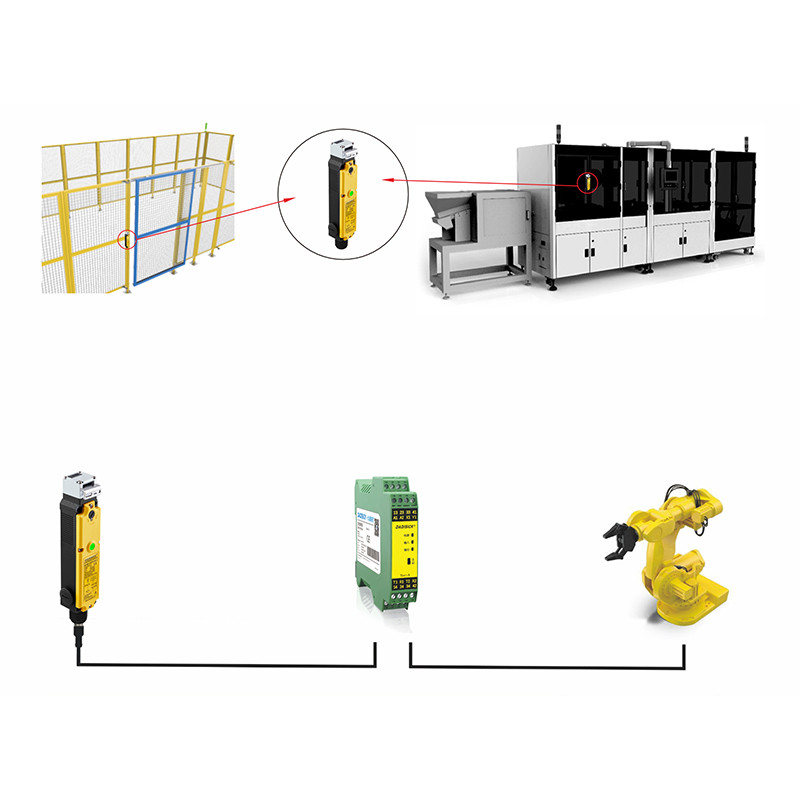
Common Faults and Troubleshooting of Industrial Safety Relays
- Share
- Issue Time
- Oct 9,2024
Summary
Industrial safety relays ensure operator safety by controlling electrical circuits. Common faults include abnormal power supply, mechanical failure, coil overheating, and maloperation. Troubleshooting involves checking power supply, contacts, mechanical parts, and control signals. Use multimeters and lubricants. Replace damaged components or relay as needed. Follow safety regulations during troubleshooting.

Safety relays play a vital role in industrial electrical control systems. They are not only key control components in the safety loop, but are also responsible for quickly cutting off the circuit when potential danger is detected to ensure the safety of equipment operators. However, due to the complex and changeable working environment, improper operation or aging of components, safety relays will inevitably have various faults during operation. This article aims to deeply explore the common fault types of safety relays and their troubleshooting methods, in order to provide practical reference for industrial electrical safety managers.
Emergency Stop Button-Related Safety Relay Faults
Common Faults:
1. Emergency Stop Button Fails to Trigger Safety Shutdown
Possible Causes:
▪️Oxidized or stuck contacts in the button;
▪️Loose wiring or open circuit;
▪️Faulty input channel on the safety relay.
Troubleshooting:
▪️Check if the emergency stop button is properly reset (rotated or pulled out);
▪️Test contact continuity using a multimeter;
▪️Inspect wiring terminals for tightness and check for cable damage.
2. System Fails to Restore After Emergency Stop Reset
Possible Causes:
▪️Safety relay not reset correctly (manual/auto reset required);
▪️Other safety devices (e.g., door switches) remain triggered.
Troubleshooting:
▪️Confirm the relay’s reset logic (manual reset requires pressing the reset button);
▪️Verify all interconnected safety devices are cleared from alarm status.

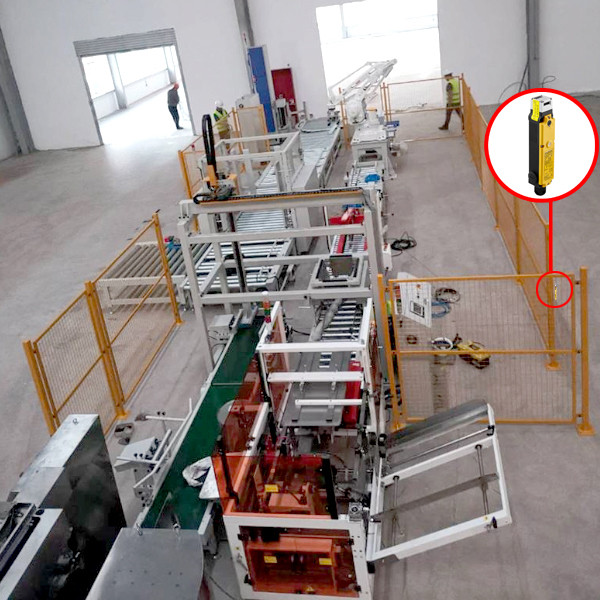
Safety Door Switch-Related Safety Relay Faults
Common Faults:
1. System Remains in Alarm After Door Closure
Possible Causes:
▪️Misaligned door switch prevents micro-switch activation;
▪️Dirty or worn contacts;
▪️Power supply failure to the electromagnetic lock.
Troubleshooting:
▪️Adjust the door switch position to ensure mechanical engagement;
▪️Clean contacts or replace damaged switches;
▪️Check power supply voltage to the electromagnetic lock (typically 24V DC).
2. Frequent False Triggers
Possible Causes:
▪️Vibration or mechanical shocks loosening the switch;
▪️Inadequate ingress protection (e.g., dust, oil contamination).
Troubleshooting:
▪️Reinforce mounting and add anti-vibration measures;
▪️Use higher IP-rated switches and clean regularly.
Safety Light Curtain-Related Safety Relay Faults
Common Faults:
1. The light curtain is not blocked, but the safety relay is frequently tripped.
Possible Causes:
▪️Misalignment between emitter and receiver;
▪️Reflective interference (e.g., from metal surfaces);
▪️The light curtain lens is contaminated (dust or oil blocks the light beam).
Troubleshooting:
▪️Realign the light curtain to ensure beam continuity;
▪️Install shields or reposition to avoid reflective surfaces;
▪️Clean lenses with a soft cloth.
2. Light Curtain Fails to Detect Obstructions
Possible Causes:
▪️Power supply failure;
▪️Broken or shorted signal cables;
▪️Internal circuit damage.
Troubleshooting:
▪️Verify power supply voltage (typically 24V DC);
▪️Test signal output with a multimeter;
▪️Replace faulty light curtain modules.


General Faults (Safety Relay Itself)
1. Abnormal power supply: Due to the power supply voltage being too high or too low, the safety relay cannot work properly, resulting in circuit abnormality.
2. Troubleshooting method: Use a multimeter to measure whether the power supply voltage is within the rated range specified by the safety relay. You need to adjust the power supply output voltage or replace the appropriate power supply, if the voltage is abnormal.
3. Mechanical failure: The safety relay is subjected to vibration or collision during operation, causing the mechanical parts (such as springs, transmission mechanisms, etc.) to be damaged or stuck, resulting in poor contact or failure of the contacts.
4. Troubleshooting method: Check the contact condition of the contacts to confirm whether there is poor contact or failure by multimeter. Check whether the mechanical parts of the relay are damaged or stuck. replace them if damaged. For the problem of jamming caused by lack of lubrication, you can add a proper amount of lubricating oil for lubrication. If the contact is seriously damaged, you need to replace the new safety relay in time.
5. Coil overheating: The coil part of the safety relay is overheating, which may even be accompanied by a strange smell.
Troubleshooting method: Make sure the power supply voltage does not exceed the rated voltage of the safety relay to avoid overheating. If the ambient temperature is high, additional cooling measures should be taken, such as increasing ventilation or using a heat sink.
Maloperation: The safety relay operates automatically without receiving a valid control signal.
6. Troubleshooting method: Check whether there are external factors such as electromagnetic interference and vibration that cause the relay to malfunction. Use a multimeter or other tool to check whether there is a short circuit or open circuit in the internal circuit of the relay. If the specific cause cannot be determined or the fault recurs, we is recommended to contact the manufacturer or replace the safety relay.
There are many kinds of fault phenomena in safety relays, but most of them can be located and eliminated by carefully checking the power supply, control signal, contacts, load and mechanical parts. When troubleshooting, relevant safety regulations should be followed to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
Supports up to 6 safety device inputs, 2 relay safety outputs, and 4 semiconductor safety outputs. Configurable via setup software to define safety control logic, meeting various on-site application requirements.
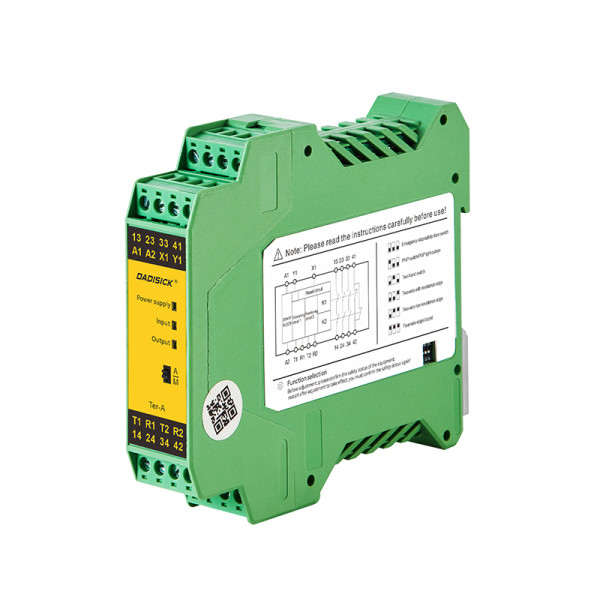
A safety relay with 3 NO (normally open) safety output contacts and 1 NC (normally closed) auxiliary output contact. It supports single or dual-channel operation, manual or automatic reset, and features short-circuit monitoring between channels.
3NO + 1NC safety contacts
Auto/manual reset option
Redundant self-monitoring circuit ensures reliability
Automatic contact testing in each cycle
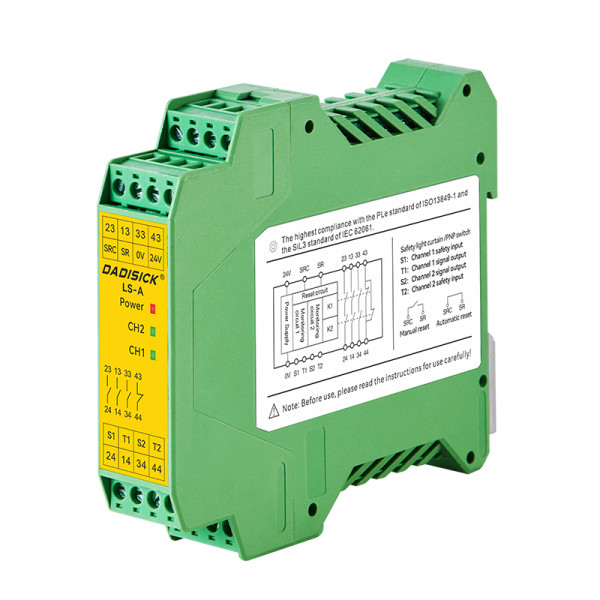
3NO + 1NC safety contacts
Auto/manual reset option
Configurable for E-stop, light curtains, door locks, and two-hand control switches