How to Choose the Right Non-contact Safety Switch: Types, Advantages, and Applications
- Share
- publisher
- Zoe
- Issue Time
- Aug 8,2025
Summary
Explore the comprehensive guide to non-contact safety switches, covering magnetic and RFID types, their unparalleled benefits like enhanced safety, reduced wear, and suitability for harsh environments, and diverse applications in industrial automation, machine guarding, and more.

What Is A Non-Contact Safety Switch?
A non-contact safety switch is a safety interlock device that detects whether a door or protective device is closed without physical contact and triggers a safety shutdown signal in the event of an abnormality. It monitors status through magnetic fields, RFID (radio frequency identification), or other non-contact technologies and is widely used in industrial equipment safety door monitoring.
Basic definition of non-contact safety switches
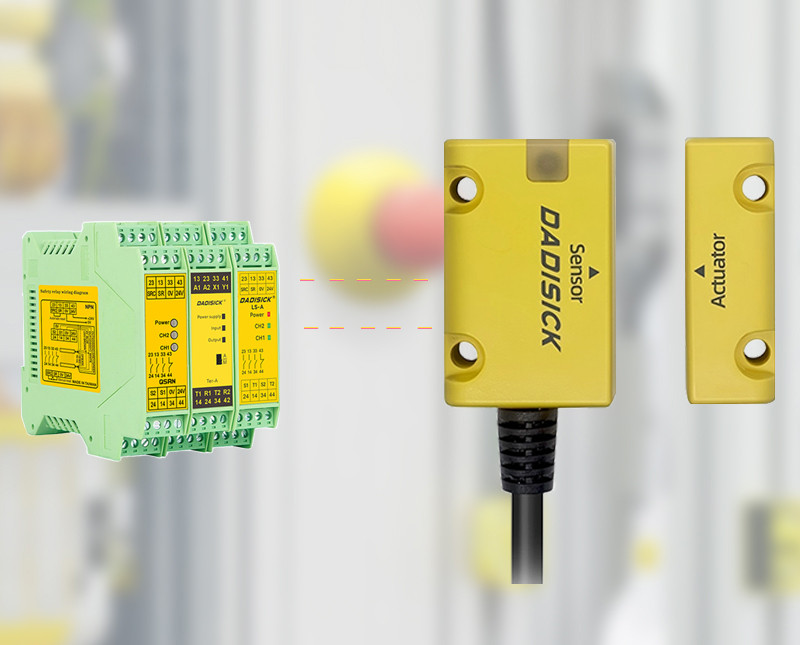
Non-contact safety switches consist of two parts:
● Actuator (installed on the door)
● Switch body (installed on the frame)
There is no need for physical contact between the two parts. Instead, they use magnetic fields or wireless signals to determine whether the door is closed.


Working principle of non-contact safety switches
There are currently two main technologies:
● Reed switch type: Uses changes in the magnetic field of a magnet to trigger the reed switch. When the door is closed, the magnetic field strengthens and the switch conducts; when the door is opened, the magnetic field weakens and the switch disconnects.
● RFID type: Uses radio frequency identification technology. The actuator has a built-in RFID chip, and the switch body reads and verifies the ID to confirm whether the door is closed.
Major Features
✅No Mechanical Wear: Due to non-contact operation, it offers a long lifespan and is maintenance-free.
✅Dustproof and Waterproof: The smooth surface makes it suitable for clean environments such as food and pharmaceutical industries.
✅Tamper-proof: The RFID model supports unique code pairing, preventing illegal bypassing with magnets or tools.
✅Flexible Installation: It has low requirements for door types (sliding, swing) and installation precision.
What Are The Different Types Of Non-Contact Safety Switches?
Non-contact safety switches can be primarily categorized into the following types based on their detection principles, safety levels, and application scenarios:
Detection Principles
● Reed Switch Type: Utilizes magnetic coupling between a magnet and a reed switch for detection, featuring a simple structure and low cost. To prevent deception by ordinary magnets, multiple reed switch combinations are typically used for verification.
● RFID type: Wireless communication is established between an RFID reader/writer and a uniquely encoded RFID tag (actuator), offering high tamper-resistance and enhanced security.
Encoding Method
● Unique encoding type (single-code type): The sensor only accepts the uniquely matched actuator encoding (similar to a key-lock principle), providing the highest tamper-resistance.
● Universal Encoding Type (Multi-Code Type): Allows multiple actuators with the same code to trigger, offering high flexibility and suitability for bulk applications
Security Level
● Type 3: Complies with ISO 14119 standards, providing medium security level, suitable for general-risk environments
● Type 4: Highest security level, featuring fault detection and tamper-proof functions, suitable for high-risk environments
Typical product examples
● Reed switch type: Schmersal BNS 36 series, Omron D40Z series
● RFID type: IDEC HS3A (unique coding type and universal coding type available), Pilz PSENcode, DADISICK OX-R1 series
Selection Tips
● High safety requirements: Prioritize RFID-type Type 4 rating (e.g., uniquely coded PSENcode).
● Cost-sensitive scenarios: Reed switch-type Type 3 is sufficient, but be mindful of magnetic interference issues.
Applications of Non-Contact Safety Switches
Non-contact safety switches, with their “zero contact, no wear” features, have penetrated almost all industrial scenarios requiring “door status monitoring + personnel protection.” The following summarizes their mainstream applications across three dimensions: industry → typical equipment → specific functions, and provides practical case studies and selection tips.
Discrete Manufacturing (Robots, Machine Tools, Injection Molding)
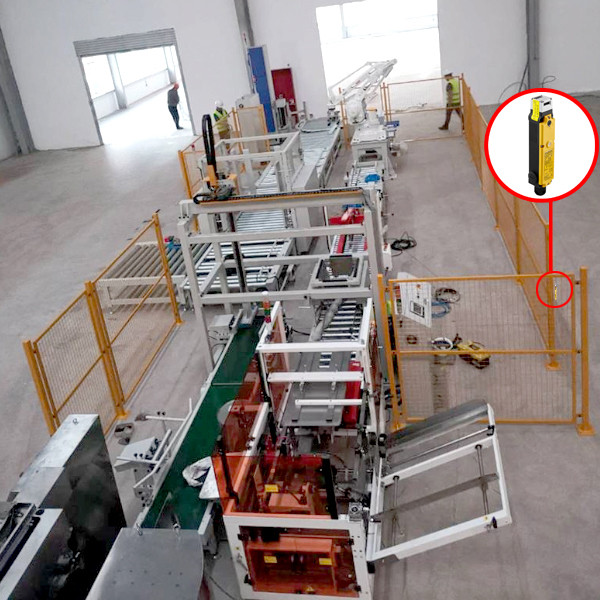
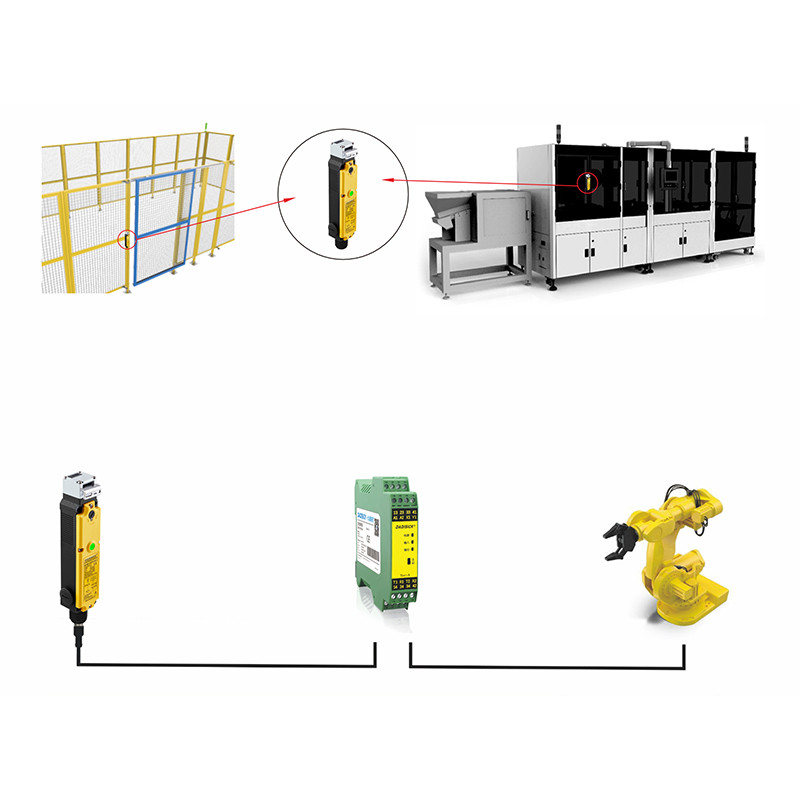
• Robot Enclosure Safety Doors
– Requirements: Frequent opening/closing, tamper-proof, and prevention of accidental robot startup.
– Commonly used: RFID-type unique encoding switches (e.g., Pilz PSENcode, DADISICK OX-R1), safety rating PL e / SIL 3.
• Front doors and top covers of injection molding machines/die-casting machines
– Requirements: High temperatures and oil contamination in the mold area, leading to mechanical contact failure.
– Commonly used: IP67/IP69K magnetic induction switches (e.g., DSR series), which can be directly rinsed.
• CNC machining center side doors
– Requirements: Reliable detection even with minor door shaking or misalignment.
– Commonly used: Wide magnetic gap reed switches or RFID wide-range switches, which can operate even with ±5 mm installation offset.
Food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics
• Filling machine/slicing machine safety guard
– Requirements: Stainless steel housing, no dead corners, easy to clean; prevents bacterial residue.
– Commonly used: 316L stainless steel housing, IP69K magnetic encoder switches (e.g., IDEM BMR, DADISICK OXC series).
• Sterile isolator glove box door
– Requirements: Avoid dirt accumulation in gaps of conventional switches; must withstand hydrogen peroxide disinfection.
– Commonly used: Fully enclosed flat-type non-contact switches with weldable surfaces.
Logistics and AGV
• Automatic warehouse maintenance doors, AGV channel door
– Requirements: Multiple doors in series, saving wiring, and remote communication with PLC.
– Commonly used: Series-type RFID switches (e.g., Omron D40Z, up to 30 switches in series).
• Smart forklift guardrails
– Requirements: High vibration, battery interference; requires wide voltage range of 10–30 VDC.
– Commonly used: Magnetic induction type, with built-in self-check signal, resistant to electromagnetic interference.
Energy and Utilities
• Wind turbine blade control cabinets, high-voltage distribution cabinet doors
– Requirements: Tamper-proof, outdoor high and low temperatures (-40 °C to +85 °C).
– Commonly used: Metal housing RFID unique coding switches with LED diagnostics.
• Battery production line drying room
– Requirements: Low dust, avoid mechanical wear and tear that generates particles.
– Commonly used: Fully plastic-encapsulated magnetic induction switch, no risk of sparking from contacts.
Cleanrooms and Semiconductors
• Wafer handling robot enclosure
– Requirements: Class 100 cleanliness, switch itself does not generate dust.
– Commonly used: Magnetic induction type, non-contact to avoid particles; surface made of anodized aluminum or PEEK material.
• Semiconductor cutting equipment front door
– Requirements: Avoid cross-contamination caused by operators pressing the switch while wearing dust-free gloves.
– Commonly used: Near-infrared reflective non-contact button (e.g., IDEC CW1H)
Special scenario extensions
• Explosion-proof zone (Zone 2/22)
– Requirements: ATEX/IECEx certification.
– Solution: Select magnetic induction Ex e enclosure type, or RFID type with intrinsically safe circuit.
• Multi-position monitoring
– Requirements: The same door needs to detect three states: “fully open/half open/closed.”
– Solution: Three-position RFID switch (e.g., PSENcode csx.19)
Selection Tips
1. Determine the “risk level” first: If there is a risk of serious injury or death, prioritize RFID unique coding + PL e/SIL 3.
2. Determine the “environmental level” next: IP69K for high-pressure washing; easy-to-clean housing for cleanrooms; check ATEX certification for explosion-proof zones.
3. Finally, consider the “installation conditions”: If the door has significant vibration, choose a magnetic induction wide-gap type; if serial connection is required, choose a model supporting daisy-chain communication.
In summary: Any location with a “protective door/cover” where traditional mechanical switches may experience wear, contamination, misalignment, or intentional bypassing can consider replacing them with non-contact safety switches.
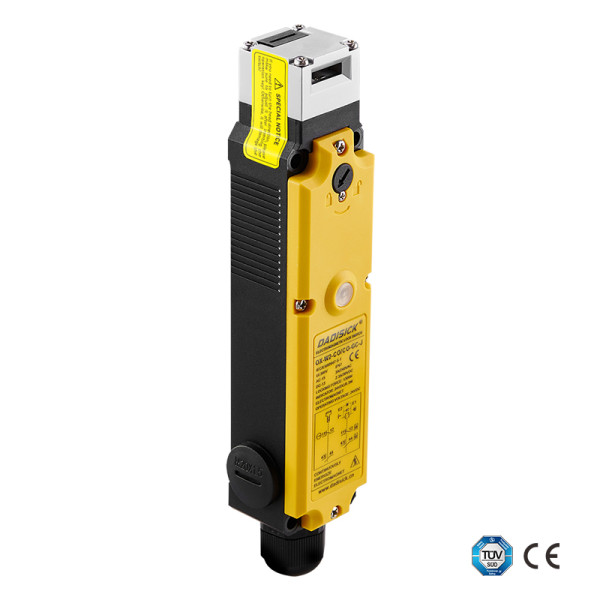
Recommended OX-R1 Series Non Contact RFIF Coded Safety Switches
The OX-R1 series RFID safety switches are based on RFID technology and offer advantages over mechanical or magnetic switches, including secure detection (with unique coding), strong interference resistance, and reliable safety. The use of safe dual-channel output technology achieves safety level PLe, effectively preventing false negatives, false positives, or unauthorized manual activation. These switches can be used in conjunction with safety door locks. | ||||
Safety standards | ISO13849-1, IEC/EN60947-5-1, IEC/EN60947-5-3 | |||
Safety classification | Class 4 switch with IS0 13849-1/suitable for PLe/PLd | |||
Certification | CE | |||
Horizontal distance | Conduction, min: 10 mm | |||
Vertical distance | Conduction, min: 8 mm | |||
Operating voltage | 24 V DC±15% | |||
Operating current | 30 mA | |||
Output current | 150 mA | |||
Response time | 60 ms | |||
Protection level | IP65, IP67 (customized)\IP68 (customized) | |||
Operating frequency | 1 Hz | |||
Operating temperature | -10 ~ +55℃ | |||
Relative humidity | 5 ~ 95% | |||
Material | Anti-flame retardant thermoplastic | |||
OX-R1-FN-S-P1 | 4-core direct wiring dual NPN output 2M line | ||
OX-R1-FP-S-P1 | 4-core direct wiring dual PNP output 2M line | ||
OX-R1-EN-S-P1 | 6-core direct wiring dual NPN output with cascade 2M line | ||
OX-R1-EP-S-P1 | 6-core direct wiring dual PNP output with cascade 2M line | ||
OX-R1-FN-D-P1 | 4-core direct wiring dual NPN output 2M line, Actuator with unique code | ||
OX-R1-FP-D-P1 | 4-core direct wiring dual PNP output 2M line, Actuator with unique code | ||
OX-R1-EN-D-P1 | 6-core direct wiring dual NPN output with cascade 2M line, Actuator with unique code | ||
OX-R1-EP-D-P1 | 6-core direct wiring dual PNP output with cascade 2M line, Actuator with unique code | ||
Related Safety Interlock Devices
Used for monitoring places such as safety doors and windows.
Safety door switch providing robust security and reliable access control.
Protecting your facility and employees.
Used for monitoring places such as safety doors and windows.