Safety Light Curtains: Why Normally Closed Circuits Are the Foundation of Safety
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 19,2025
Summary
Learn why normally closed circuits are essential for safety light curtains, ensuring fail-safe operation and compliance with industrial safety standards.

Safety light curtains play a critical role in modern industrial safety systems, protecting operators from hazardous machine motion without restricting productivity. While optical resolution and response time are often discussed, the electrical output logic—especially the use of normally closed (NC) circuits—is the true foundation of functional safety. This article explains why normally closed circuits are essential for fail-safe operation, how they comply with international safety standards, and how Dadisick safety light curtains implement these principles in real industrial applications.
What Is a Safety Light Curtain?
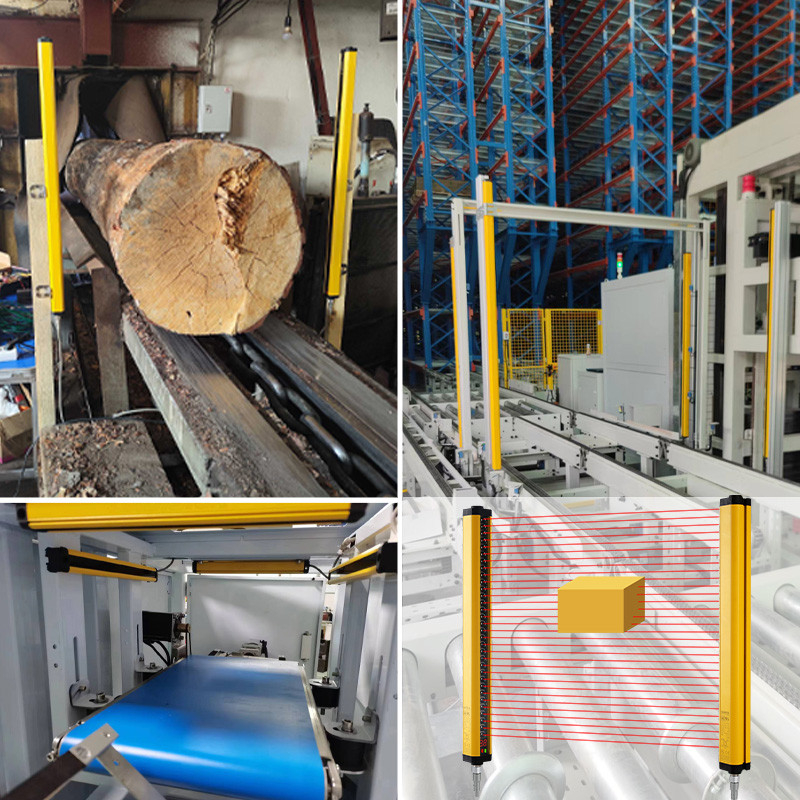
A safety light curtain is an optoelectronic protective device that creates an invisible infrared beam field across a hazardous area. When a person or object interrupts the beam, the system immediately sends a stop signal to the machine controller, preventing injury or equipment damage. Due to safety light curtains providing non-contact protection, they are widely used in presses, robotic cells, automated assembly lines, packaging machines, and conveyor systems—especially where frequent operator access is required. To understand different protection resolutions, detection heights, and application scenarios, refer to DADISICK's safety light curtain product categories.
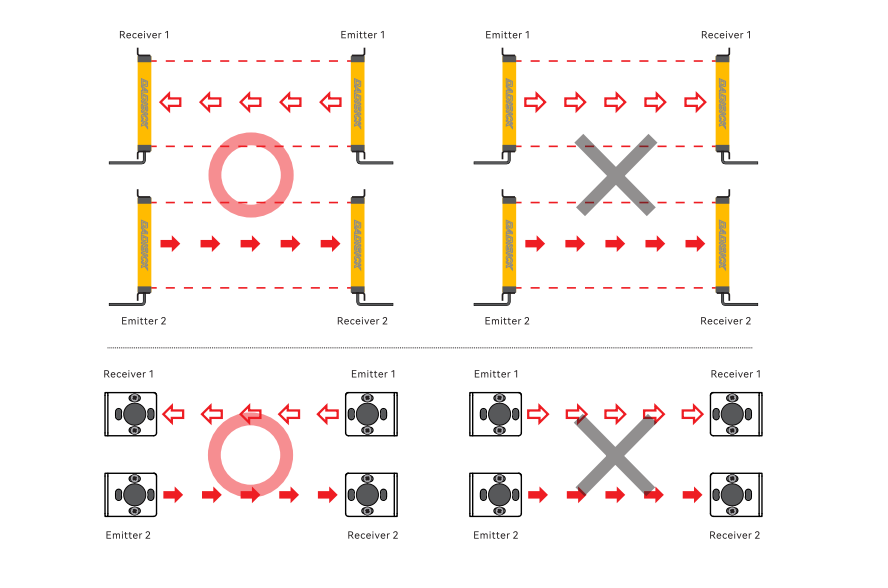
Normally Closed vs. Normally Open Circuits: The Key Difference


In industrial safety systems, output circuits are generally classified as normally closed (NC) or normally open (NO).
· Normally Closed (NC):
The circuit remains closed during normal operation. Any abnormal condition—power loss, cable break, sensor failure—opens the circuit and triggers a stop signal.
· Normally Open (NO):
The circuit remains open during normal operation and only closes when activated. Certain faults may not be detected immediately.
From a safety engineering perspective, NC circuits are preferred because they are inherently fail-safe.
Why Normally Closed Circuits Are Essential for Safety Light Curtains
Fail-Safe Behavior by Default
Continuous Monitoring of the Safety Loop
NC circuits allow safety relays and safety PLCs to monitor circuit integrity continuously. Any unexpected open state—whether caused by vibration, connector failure, or environmental stress—is immediately detected. This continuous monitoring capability is essential for achieving higher performance levels, such as PL d or PL e in accordance with ISO 13849-1. Detailed wiring logic and monitoring concepts can be found in DADISICK's safety light curtain technical documentation.
Compliance with International Safety Standards
International machinery safety standards are built on the assumption that systems must transition to a safe condition when faults occur. As a result, normally closed circuits are strongly recommended or required in standards such as:
· ISO 13849-1 – Safety-related parts of control systems
· IEC 62061 / IEC 61508 – Functional safety of electrical systems
Using NC outputs is therefore not just best practice—it is often a compliance requirement in regulated industrial environments.
NC vs. NO Circuits: Practical Comparison
| Feature | Normally Closed (NC) | Normally Open (NO |
| Default state | Closed (monitored) | Open (not monitored) |
| Power loss response | Immediate safe stop | Uncertain |
| Cable break detection | Instant | Often undetected |
Suitability for safety systems | Guaranteed | Not guaranteed |
This comparison clearly explains why normally closed circuits are considered the foundation of safety light curtain design.
How Dadisick Safety Light Curtains Apply NC Principles
Dadisick safety light curtains are engineered with normally closed safety outputs to ensure reliable machine stopping under all fault conditions. When integrated with safety relays or safety PLCs, they offer:
· Fast and reliable response to beam interruption
· Automatic detection of power or wiring faults
· Compatibility with modern functional safety architectures
These design choices help machine builders and end users reduce residual risk while maintaining high productivity. Discover more about the available configurations and applications offered by DADISICK's industrial safety sensor solutions.
Conclusion: NC Circuits Are the True Safety Foundation
For safety light curtain systems and broader machine safety circuits, normally closed contacts are the foundation of a reliable safety design. They enforce a default safe state on failure, enable effective fault detection, and support redundancy and self-monitoring — all essential aspects of functional safety engineering. Understanding the role of NC circuits is critical for designers, integrators, and safety professionals who aim to build systems that not only protect operators but also comply with international safety standards.
Related Safety Devices
Beam spacing:40mm
Number of optical axes:20
Protection height:760mm
Safety sensors for machines output (OSSD):2 PNP
Multifunctional safety relay, providing automatic/manual reset configuration and multifunctional configuration DIP switch, used for industrial field monitoring of various signals with high safety requirements.
5m distance, A technique that uses a laser beam to measure distance and create detailed maps of objects and environments.
Used for monitoring places such as safety doors and windows.
Similar Posts You May Be Interested in